4412 lines
290 KiB
Markdown
4412 lines
290 KiB
Markdown
# KiBot (formerly KiPlot)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/actions)
|
|
[](https://coveralls.io/github/INTI-CMNB/KiBot?branch=master)
|
|
[](https://pypi.org/project/kibot/)
|
|
[](https://www.paypal.com/donate/?hosted_button_id=K2T86GDTTMRPL)
|
|
|
|
# **This is the documentation for the current development KiBot, not yet released.**
|
|
|
|
|
|
**Important for CI/CD**:
|
|
- We are now uploading docker images to GitHub, the new tags are much more simple.
|
|
Consult: [Usage for CI/CD](#usage-for-cicd)
|
|
- The GitHub actions with KiCad 6 support are tagged as `v2_k6` (stable) and `v2_dk6` (development).
|
|
Consult: [Github Actions tags](#github-actions-tags)
|
|
|
|
**Important note about PcbDraw 1.0.0**
|
|
- This release is incompatible with 0.9.0, I'm trying to fix some issues in the upstream package.
|
|
|
|
**New on v1.4.0**
|
|
- PCB_Variant and Copy_Files outputs
|
|
- urlify and field_modify filters
|
|
- Basic pre-processing
|
|
|
|
## Index
|
|
|
|
* [Introduction](#introduction)
|
|
* [Installation](#installation)
|
|
* [Dependencies](#dependencies)
|
|
* [Installation on Ubuntu or Debian](#installation-on-ubuntu-or-debian)
|
|
* [Installation using pip](#installation-using-pip)
|
|
* [Notes about virtualenv](#notes-about-virtualenv)
|
|
* [Installation on other targets](#installation-on-other-targets)
|
|
* [Configuration](#configuration)
|
|
* [Quick start](#quick-start)
|
|
* [The header](#the-header)
|
|
* [The *preflight* section](#the-preflight-section)
|
|
* [Supported *preflight* options](#supported-preflight-options)
|
|
* [More about *pcb_replace* and *sch_replace*](#more-about-pcb_replace-and-sch_replace)
|
|
* [Filtering DRC and ERC errors](#filtering-drc-and-erc-errors)
|
|
* [Default global options](#default-global-options)
|
|
* [Default *output* option](#default-output-option)
|
|
* [Default *dir* option](#default-dir-option)
|
|
* [Default *variant* option](#default-variant-option)
|
|
* [Default *units* option](#default-units-option)
|
|
* [Output directory option](#output-directory-option)
|
|
* [Date format option](#date-format-option)
|
|
* [PCB details options](#pcb-details-options)
|
|
* [Filtering KiBot warnings](#filtering-kibot-warnings)
|
|
* [All available global options](#all-available-global-options)
|
|
* [Filters and variants](#filters-and-variants)
|
|
* [Supported filters](#supported-filters)
|
|
* [Examples for filters](#examples-for-filters)
|
|
* [Built-in filters](#built-in-filters)
|
|
* [Supported variants](#supported-variants)
|
|
* [Changing the 3D model, simple mechanism](#changing-the-3d-model-simple-mechanism)
|
|
* [Changing the 3D model, complex mechanism](#changing-the-3d-model-complex-mechanism)
|
|
* [DNF and DNC internal keys](#dnf-and-dnc-internal-keys)
|
|
* [The *outputs* section](#the-outputs-section)
|
|
* [Specifying the layers](#specifying-the-layers)
|
|
* [Supported outputs](#supported-outputs)
|
|
* [Consolidating BoMs](#consolidating-boms)
|
|
* [Importing outputs from another file](#importing-outputs-from-another-file)
|
|
* [Using other output as base for a new one](#using-other-output-as-base-for-a-new-one)
|
|
* [Importing filters and variants from another file](#importing-filters-and-variants-from-another-file)
|
|
* [Doing YAML substitution or preprocessing](#doing-yaml-substitution-or-preprocessing)
|
|
* [Usage](#usage)
|
|
* [Usage for CI/CD](#usage-for-cicd)
|
|
* [Github Actions](#usage-of-github-actions)
|
|
* [Github Actions tags](#github-actions-tags)
|
|
* [Contributing](#contributing)
|
|
* [Notes about Gerber format](#notes-about-gerber-format)
|
|
* [Notes about the position file](#notes-about-the-position-file)
|
|
* [XYRS files](#xyrs-files)
|
|
* [Notes about 3D models](#notes-about-3d-models)
|
|
* [Credits](#credits)
|
|
|
|
## Introduction
|
|
|
|
KiBot is a program which helps you to generate the fabrication and
|
|
documentation files for your KiCad projects easily, repeatable, and
|
|
most of all, scriptably. This means you can use a Makefile to export
|
|
your KiCad PCBs just as needed, or do it in a CI/CD environment.
|
|
|
|
For example, it's common that you might want for each board rev:
|
|
|
|
* Check ERC/DRC one last time (using [KiCad Automation Scripts](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad-automation-scripts/))
|
|
* Gerbers, drills and drill maps for a fab in their favourite format
|
|
* Fab docs for the assembler, including the BoM (Bill of Materials), costs spreadsheet and board view
|
|
* Pick and place files
|
|
* PCB 3D model in STEP format
|
|
* PCB 3D render in PNG format
|
|
* Compare PCB/SCHs
|
|
|
|
You want to do this in a one-touch way, and make sure everything you need to
|
|
do so is securely saved in version control, not on the back of an old
|
|
datasheet.
|
|
|
|
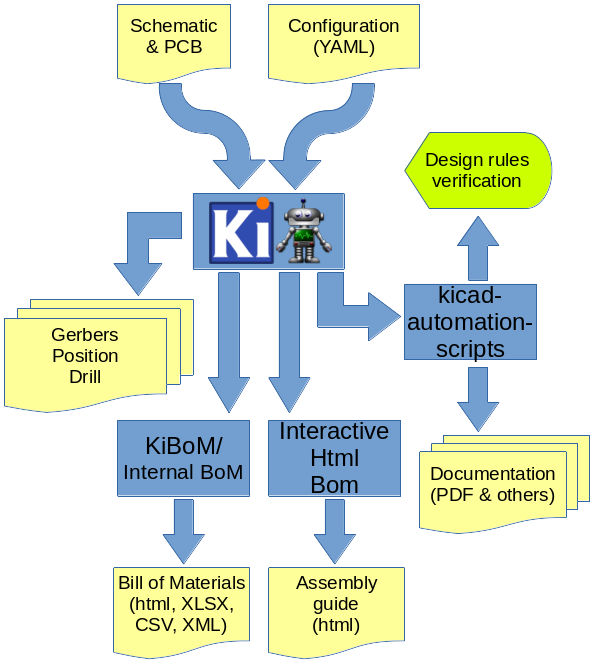
KiBot lets you do this. The following picture depicts the data flow:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If you want to see this concept applied to a real world project visit the [Spora CI/CD](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad-ci-test-spora) example.
|
|
|
|
## Installation
|
|
|
|
KiBot main target is Linux, but some users successfully use it on Windows. For Windows you'll need to install tools to mimic a Linux environment.
|
|
Running KiBot on MacOSX should be possible now that KiCad migrated to Python 3.x.
|
|
|
|
You can also run KiBot using docker images in a CI/CD environment like GitHub or GitLab. In this case you don't need to install anything locally.
|
|
|
|
### Dependencies
|
|
|
|
Notes:
|
|
- When installing from the [Debian repo](https://set-soft.github.io/debian/) you don't need to worry about dependencies, just pay attention to *recommended* and *suggested* packages.
|
|
- When installing using `pip` the dependencies marked with  will be automatically installed.
|
|
- The dependencies marked with  can be downloaded on-demand by KiBot.
|
|
Note this is experimental and is mostly oriented to 64 bits Linux systems.
|
|
- The `kibot-check` tool can help you to know which dependencies are missing.
|
|
- Note that on some systems (i.e. Debian) ImageMagick disables PDF manipulation in its `policy.xml` file.
|
|
Comment or remove lines like this: `<policy domain="coder" rights="none" pattern="PDF" />` (On Debian: `/etc/ImageMagick-6/policy.xml`)
|
|
-  Link to Debian stable package.
|
|
-  This is a Python module, not a separated tool.
|
|
-  This is an independent tool, can be a binary or a Python script.
|
|
|
|
[**PyYAML**](https://pypi.org/project/PyYAML/) [](https://pypi.org/project/PyYAML/) [](https://pypi.org/project/PyYAML/) [](https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/python3-yaml)
|
|
- Mandatory
|
|
|
|
[**Requests**](https://pypi.org/project/Requests/) [](https://pypi.org/project/Requests/) [](https://pypi.org/project/Requests/) [](https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/python3-requests)
|
|
- Mandatory
|
|
|
|
[**KiCad Automation tools**](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiAuto) v2.0.4 [](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiAuto) 
|
|
- Mandatory for: `gencad`, `netlist`, `pdf_pcb_print`, `pdf_sch_print`, `render_3d`, `run_drc`, `run_erc`, `step`, `svg_pcb_print`, `svg_sch_print`, `update_xml`
|
|
- Optional to:
|
|
- Compare schematics for `diff` (v2.0.0)
|
|
- Show KiAuto installation information for `info` (v2.0.0)
|
|
- Print the page frame in GUI mode for `pcb_print` (v1.6.7)
|
|
|
|
[**KiCost**](https://github.com/hildogjr/KiCost) v1.1.8 [](https://github.com/hildogjr/KiCost) 
|
|
- Mandatory for `kicost`
|
|
- Optional to find components costs and specs for `bom`
|
|
|
|
[**PcbDraw**](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/pcbdraw) v0.9.0.3 (<1.0) [](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/pcbdraw) 
|
|
- Mandatory for `pcbdraw`
|
|
- Optional to create realistic solder masks for `pcb_print`
|
|
- Note: Currently the upstream version is broken, please use the mentioned fork
|
|
|
|
[**Interactive HTML BoM**](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/InteractiveHtmlBom) v2.4.1.4 [](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/InteractiveHtmlBom) 
|
|
- Mandatory for `ibom`
|
|
|
|
[**KiBoM**](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBoM) v1.8.0 [](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBoM) 
|
|
- Mandatory for `kibom`
|
|
|
|
[**KiCad PCB/SCH Diff**](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiDiff) v2.4.2 [](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiDiff) 
|
|
- Mandatory for `diff`
|
|
|
|
[**LXML**](https://pypi.org/project/LXML/) [](https://pypi.org/project/LXML/) [](https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/python3-lxml) 
|
|
- Mandatory for `pcb_print`
|
|
|
|
[**QRCodeGen**](https://pypi.org/project/QRCodeGen/) [](https://pypi.org/project/QRCodeGen/) [](https://pypi.org/project/QRCodeGen/) [](https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/python3-qrcodegen) 
|
|
- Mandatory for `qr_lib`
|
|
|
|
[**Colorama**](https://pypi.org/project/Colorama/) [](https://pypi.org/project/Colorama/) [](https://pypi.org/project/Colorama/) [](https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/python3-colorama)
|
|
- Optional to get color messages in a portable way for general use
|
|
|
|
[**Git**](https://git-scm.com/) [](https://git-scm.com/) [](https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/git) 
|
|
- Optional to:
|
|
- Compare with files in the repo for `diff`
|
|
- Find commit hash and/or date for `pcb_replace`
|
|
- Find commit hash and/or date for `sch_replace`
|
|
- Find commit hash and/or date for `set_text_variables`
|
|
|
|
[**RSVG tools**](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/librsvg) [](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/librsvg) [](https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/librsvg2-bin) 
|
|
- Optional to:
|
|
- Create outputs preview for `navigate_results`
|
|
- Create PNG icons for `navigate_results`
|
|
- Create PDF, PNG, PS and EPS formats for `pcb_print`
|
|
- Create PNG and JPG images for `pcbdraw`
|
|
|
|
[**ImageMagick**](https://imagemagick.org/) [](https://imagemagick.org/) [](https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/imagemagick) 
|
|
- Optional to:
|
|
- Create outputs preview for `navigate_results`
|
|
- Create monochrome prints and scaled PNG files for `pcb_print`
|
|
- Create JPG images for `pcbdraw`
|
|
|
|
[**Ghostscript**](https://www.ghostscript.com/) [](https://www.ghostscript.com/) [](https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/ghostscript) 
|
|
- Optional to:
|
|
- Create outputs preview for `navigate_results`
|
|
- Create PNG, PS and EPS formats for `pcb_print`
|
|
|
|
[**Pandoc**](https://pandoc.org/) [](https://pandoc.org/) [](https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/pandoc)
|
|
- Optional to create PDF/ODF/DOCX files for `report`
|
|
- Note: In CI/CD environments: the `kicad_auto_test` docker image contains it.
|
|
|
|
[**RAR**](https://www.rarlab.com/) [](https://www.rarlab.com/) [](https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/rar) 
|
|
- Optional to compress in RAR format for `compress`
|
|
|
|
[**XLSXWriter**](https://pypi.org/project/XLSXWriter/) [](https://pypi.org/project/XLSXWriter/) [](https://pypi.org/project/XLSXWriter/) [](https://packages.debian.org/bullseye/python3-xlsxwriter) 
|
|
- Optional to create XLSX files for `bom`
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Installation on Ubuntu or Debian
|
|
|
|
The easiest way is to use the [repo](https://set-soft.github.io/debian/), but if you want to manually install the individual `.deb` files you can:
|
|
|
|
Get the Debian package from the [releases section](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/releases) and run:
|
|
```shell
|
|
sudo apt install ./kibot*_all.deb
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
**Important note**: Sometimes the release needs another packages that aren't part of the stable Debian distribution.
|
|
In this case the packages are also included in the release page. As an example version 0.6.0 needs:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
sudo apt install ./python3-mcpy_2.0.2-1_all.deb ./kibot_0.6.0-1_all.deb
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
**Important note**: The [KiCad Automation Scripts](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad-automation-scripts/) packages are a mandatory dependency.
|
|
The [KiBoM](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBoM), [InteractiveHtmlBom](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/InteractiveHtmlBom) and [PcbDraw](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/PcbDraw) are recommended.
|
|
|
|
### Installation using pip
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
pip install --no-compile kibot
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Note that `pip` has the dubious idea of compiling everything it downloads.
|
|
There is no advantage in doing it and it interferes with the `mcpy` macros.
|
|
Also note that in modern Linux systems `pip` was renamed to `pip3`, to avoid confusion with `pip` from Python 2.
|
|
|
|
If you are installing at system level I recommend generating the compilation caches after installing.
|
|
As `root` just run:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot --help-outputs > /dev/null
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Note that `pip` will automatically install all the needed Python dependencies.
|
|
But it won't install other interesting dependencies.
|
|
In particular you should take a look at the [KiCad Automation Scripts](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad-automation-scripts/) dependencies.
|
|
If you have a Debian based OS I strongly recommend trying to use the `.deb` packages for all the tools.
|
|
|
|
If you want to install the code only for the current user add the `--user` option.
|
|
|
|
If you want to install the last git code from GitHub using pip use:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
pip3 install --user git+https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot.git
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
You can also clone the repo, change to its directory and install using:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
pip3 install --user -e .
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
In this way you can change the code and you won't need to install again.
|
|
|
|
### Notes about virtualenv
|
|
|
|
If you try to use a Python virtual environment you'll need to find a way to make the KiCad module (`pcbnew`) available on it.
|
|
I don't know how to make it.
|
|
|
|
### Installation on other targets
|
|
|
|
- Install KiCad 5.1.6 or newer
|
|
- Install Python 3.5 or newer
|
|
- Install the Python Yaml and requests modules
|
|
- Run the script *src/kibot*
|
|
|
|
## Configuration
|
|
|
|
KiBot uses a configuration file where you can specify what *outputs* to
|
|
generate and which preflight (before *launching* the outputs generation)
|
|
actions to perform. By default you'll generate all of them, but you can specify which
|
|
ones from the command line.
|
|
|
|
The configuration file should be named using the **.kibot.yaml** suffix,
|
|
i.e. *my_project.kibot.yaml*. The format used is [YAML](https://yaml.org/).
|
|
This is basically a text file with some structure.
|
|
This file can be compressed using *gzip* file format.
|
|
|
|
If you never used YAML read the following [explanation](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/blob/master/docs/KiPlotYAML.md).
|
|
Note that the explanation could be useful even if you know YAML.
|
|
|
|
### Quick start
|
|
|
|
If you want to *learn by examples*, or you just want to take a look a what
|
|
KiBot can do, you can use the `--quick-start` command line option.
|
|
|
|
First change to the directory where your project (or projects) is located.
|
|
Now run KiBot like this:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot --quick-start
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This will look for KiCad projects starting from the current directory and
|
|
going down the directory structure. For each project found KiBot will
|
|
generate a configuration file showing some common outputs. After creating
|
|
the configuration files KiBot will start the outputs generation.
|
|
|
|
Here is an [example](https://inti-cmnb.github.io/kibot_variants_arduprog_site/Browse/t1-navigate.html)
|
|
of what's generated using the following [example repo](https://inti-cmnb.github.io/kibot_variants_arduprog/).
|
|
|
|
You can use the generated files as example of how to configure KiBot.
|
|
If you want to just generate the configuration files and not the outputs
|
|
use:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot --quick-start --dry
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If you want to know about all the possible options for all the available
|
|
outputs you can try:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot --example
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This will generate a configuration file with all the available outputs
|
|
and all their options.
|
|
|
|
### Section order
|
|
|
|
The file is divided in various sections. Some of them are optional.
|
|
|
|
The order in which they are declared is not relevant, they are interpreted in the following order:
|
|
|
|
- `kiplot`/`kibot` see [The header](#the-header)
|
|
- `import` see [Importing outputs from another file](#importing-outputs-from-another-file)
|
|
- `global` see [Default global options](#default-global-options)
|
|
- `filters` see [Filters and variants](#filters-and-variants)
|
|
- `variants` see [Filters and variants](#filters-and-variants)
|
|
- `preflight` see [The *preflight* section](#the-preflight-section)
|
|
- `outputs` see [The *outputs* section](#the-outputs-section)
|
|
|
|
### The header
|
|
|
|
All configuration files must start with:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
kibot:
|
|
version: 1
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This tells to KiBot that this file is using version 1 of the format.
|
|
|
|
### The *preflight* section
|
|
|
|
This section is used to specify tasks that will be executed before generating any output.
|
|
|
|
#### Supported preflight options:
|
|
|
|
- `annotate_pcb`: [dict] Annotates the PCB according to physical coordinates.
|
|
This preflight modifies the PCB and schematic, use it only in revision control environments.
|
|
Used to assign references according to footprint coordinates.
|
|
The project must be fully annotated first.
|
|
- `annotate_power`: [boolean=false] Annotates all power components.
|
|
This preflight modifies the schematic, use it only in revision control environments.
|
|
Used to solve ERC problems when using filters that remove power reference numbers.
|
|
- `check_zone_fills`: [boolean=false] Zones are filled before doing any operation involving PCB layers.
|
|
The original PCB remains unchanged.
|
|
- `erc_warnings`: [boolean=false] Option for `run_erc`. ERC warnings are considered errors.
|
|
- `fill_zones`: [boolean=false] Fill all zones again and save the PCB.
|
|
- `filters`: [list(dict)] A list of entries to filter out ERC/DRC messages.
|
|
Note that ignored errors will become KiBot warnings (i.e. `(W058) ...`).
|
|
To farther ignore these warnings use the `filters` option in the `global` section.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `error`: [string=''] Error id we want to exclude.
|
|
A name for KiCad 6 or a number for KiCad 5, but always a string.
|
|
- *error_number*: Alias for number.
|
|
- `filter`: [string=''] Name for the filter, for documentation purposes.
|
|
- *filter_msg*: Alias for filter.
|
|
- `number`: [number=0] Error number we want to exclude.
|
|
KiCad 5 only.
|
|
- `regex`: [string=''] Regular expression to match the text for the error we want to exclude.
|
|
- *regexp*: Alias for regex.
|
|
- `ignore_unconnected`: [boolean=false] Option for `run_drc`. Ignores the unconnected nets. Useful if you didn't finish the routing.
|
|
- `pcb_replace`: [dict] Replaces tags in the PCB. I.e. to insert the git hash or last revision date.
|
|
This is useful for KiCad 5, use `set_text_variables` when using KiCad 6.
|
|
This preflight modifies the PCB. Even when a back-up is done use it carefully.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `date_command`: [string=''] Command to get the date to use in the PCB.\
|
|
```git log -1 --format='%as' -- $KIBOT_PCB_NAME```\
|
|
Will return the date in YYYY-MM-DD format.\
|
|
```date -d @`git log -1 --format='%at' -- $KIBOT_PCB_NAME` +%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S```\
|
|
Will return the date in YYYY-MM-DD_HH-MM-SS format.\
|
|
Important: on KiCad 6 the title block data is optional.
|
|
This command will work only if you have a date in the PCB/Schematic.
|
|
- `replace_tags`: [dict|list(dict)] Tag or tags to replace.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `after`: [string=''] Text to add after the output of `command`.
|
|
- `before`: [string=''] Text to add before the output of `command`.
|
|
- `command`: [string=''] Command to execute to get the text, will be used only if `text` is empty.
|
|
KIBOT_PCB_NAME variable is the name of the current PCB.
|
|
- `tag`: [string=''] Name of the tag to replace. Use `version` for a tag named `@version@`.
|
|
- `tag_delimiter`: [string='@'] Character used to indicate the beginning and the end of a tag.
|
|
Don't change it unless you really know about KiCad's file formats.
|
|
- `text`: [string=''] Text to insert instead of the tag.
|
|
- `run_drc`: [boolean=false] Runs the DRC (Distance Rules Check). To ensure we have a valid PCB.
|
|
The report file name is controlled by the global output pattern (%i=drc %x=txt).
|
|
Note that the KiCad 6 *Test for parity between PCB and schematic* option is not supported.
|
|
If you need to check the parity use the `update_xml` preflight.
|
|
- `run_erc`: [boolean=false] Runs the ERC (Electrical Rules Check). To ensure the schematic is electrically correct.
|
|
The report file name is controlled by the global output pattern (%i=erc %x=txt).
|
|
- `sch_replace`: [dict] Replaces tags in the schematic. I.e. to insert the git hash or last revision date.
|
|
This is useful for KiCad 5, use `set_text_variables` when using KiCad 6.
|
|
This preflight modifies the schematics. Even when a back-up is done use it carefully.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `date_command`: [string=''] Command to get the date to use in the SCH.\
|
|
```git log -1 --format='%as' -- $KIBOT_SCH_NAME```\
|
|
Will return the date in YYYY-MM-DD format.\
|
|
```date -d @`git log -1 --format='%at' -- $KIBOT_SCH_NAME` +%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S```\
|
|
Will return the date in YYYY-MM-DD_HH-MM-SS format.\
|
|
Important: on KiCad 6 the title block data is optional.
|
|
This command will work only if you have a date in the SCH/Schematic.
|
|
- `replace_tags`: [dict|list(dict)] Tag or tags to replace.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `after`: [string=''] Text to add after the output of `command`.
|
|
- `before`: [string=''] Text to add before the output of `command`.
|
|
- `command`: [string=''] Command to execute to get the text, will be used only if `text` is empty.
|
|
KIBOT_SCH_NAME variable is the name of the current sheet.
|
|
KIBOT_TOP_SCH_NAME variable is the name of the top sheet.
|
|
- `tag`: [string=''] Name of the tag to replace. Use `version` for a tag named `@version@`.
|
|
- `tag_delimiter`: [string='@'] Character used to indicate the beginning and the end of a tag.
|
|
Don't change it unless you really know about KiCad's file formats.
|
|
- `text`: [string=''] Text to insert instead of the tag.
|
|
- `set_text_variables`: [dict|list(dict)] Defines KiCad 6 variables.
|
|
They are expanded using ${VARIABLE}, and stored in the project file.
|
|
This preflight replaces `pcb_replace` and `sch_replace` when using KiCad 6.
|
|
The KiCad project file is modified.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `after`: [string=''] Text to add after the output of `command`.
|
|
- `before`: [string=''] Text to add before the output of `command`.
|
|
- `command`: [string=''] Command to execute to get the text, will be used only if `text` is empty.
|
|
- `expand_kibot_patterns`: [boolean=true] Expand %X patterns. The context is `schematic`.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Name of the variable. The `version` variable will be expanded using `${version}`.
|
|
- `text`: [string=''] Text to insert instead of the variable.
|
|
- *variable*: Alias for name.
|
|
- `update_qr`: [boolean=false] Update the QR codes.
|
|
Complements the `qr_lib` output.
|
|
The KiCad 6 files and the KiCad 5 PCB needs manual update, generating a new library isn't enough.
|
|
- `update_xml`: [boolean=false|dict] Update the XML version of the BoM (Bill of Materials).
|
|
To ensure our generated BoM is up to date.
|
|
Note that this isn't needed when using the internal BoM generator (`bom`).
|
|
You can compare the PCB and schematic netlists using it.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`check_pcb_parity`**: [boolean=false] Check if the PCB and Schematic are synchronized.
|
|
This is equivalent to the *Test for parity between PCB and schematic* of the DRC dialog.
|
|
Only available for KiCad 6.
|
|
- `as_warnings`: [boolean=false] Inform the problems as warnings and don't stop.
|
|
- `enabled`: [boolean=true] Enable the update. This is the replacement for the boolean value.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Here is an example of a *preflight* section:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
preflight:
|
|
run_erc: true
|
|
update_xml: true
|
|
run_drc: true
|
|
check_zone_fills: true
|
|
ignore_unconnected: false
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### More about *pcb_replace* and *sch_replace*
|
|
|
|
These options are supposed to be used in a version control environment.
|
|
This is because, unlike other options, they modify the PCB and/or schematic and might damage them.
|
|
In a version control environment you can just roll-back the changes.
|
|
|
|
Don't be afraid, they make a back-up of the files and also tries to disable dangerous changes.
|
|
But should be used carefully. They are ideal for CI/CD environment where you don't actually commit any changes.
|
|
|
|
#### Filtering DRC and ERC errors
|
|
|
|
Sometimes KiCad reports DRC or ERC errors that you can't get rid off.
|
|
This could be just because you are part of a team including lazy people that doesn't want to take the extra effort to solve
|
|
some errors that aren't in fact errors, just small violations made on purpose. In this case you could exclude some known errors.
|
|
|
|
For this you must declare `filters` entry in the `preflight` section. Then you can add as many `filter` entries as you want.
|
|
Each filter entry has an optional description and defines to which error type is applied (`number`) and a regular expression
|
|
that the error must match to be ignored (`regex`). Like this:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
filters:
|
|
- filter: 'Optional filter description'
|
|
error: 'Error_type'
|
|
regex: 'Expression to match'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Here is a KiCad 5 example, suppose you are getting the following errors:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
** Found 1 DRC errors **
|
|
ErrType(4): Track too close to pad
|
|
@(177.185 mm, 78.315 mm): Track 1.000 mm [Net-(C3-Pad1)] on F.Cu, length: 1.591 mm
|
|
@(177.185 mm, 80.715 mm): Pad 2 of C3 on F.Cu and others
|
|
|
|
** Found 1 unconnected pads **
|
|
ErrType(2): Unconnected items
|
|
@(177.185 mm, 73.965 mm): Pad 2 of C4 on F.Cu and others
|
|
@(177.185 mm, 80.715 mm): Pad 2 of C3 on F.Cu and others
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
And you want to ignore them. You can add the following filters:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
filters:
|
|
- filter: 'Ignore C3 pad 2 too close to anything'
|
|
error: '4'
|
|
regex: 'Pad 2 of C3'
|
|
- filter: 'Ignore unconnected pad 2 of C4'
|
|
error: '2'
|
|
regex: 'Pad 2 of C4'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If you need to match text from two different lines in the error message try using `(?s)TEXT(.*)TEXT_IN_OTHER_LINE`.
|
|
|
|
If you have two or more different options for a text to match try using `(OPTION1|OPTION2)`.
|
|
|
|
A complete Python regular expressions explanation is out of the scope of this manual. For a complete reference consult the [Python manual](https://docs.python.org/3/library/re.html).
|
|
|
|
KiCad 6 uses strings to differentiate errors, use them for the `error` field. To keep compatibility you can use the `number` or `error_number` options for KiCad 5.
|
|
|
|
Note that this will ignore the errors, but they will be reported as warnings.
|
|
If you want to suppress these warnings take a look at [Filtering KiBot warnings](#filtering-kibot-warnings)
|
|
|
|
**Important note**: this will create a file named *kibot_errors.filter* in the output directory.
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Default global options
|
|
|
|
The section `global` contains default global options that affects all the outputs.
|
|
Currently only a few option are supported.
|
|
|
|
#### Default *output* option
|
|
|
|
This option controls the default file name pattern used by all the outputs. This makes all the file names coherent.
|
|
You can always choose the file name for a particular output.
|
|
|
|
The pattern uses the following expansions:
|
|
|
|
- **%c** company from pcb/sch metadata.
|
|
- **%C`n`** comments line `n` from pcb/sch metadata.
|
|
- **%d** pcb/sch date from metadata if available, file modification date otherwise.
|
|
- **%D** date the script was started.
|
|
- **%f** original pcb/sch file name without extension.
|
|
- **%F** original pcb/sch file name without extension. Including the directory part of the name.
|
|
- **%g** the `file_id` of the global variant.
|
|
- **%G** the `name` of the global variant.
|
|
- **%i** a contextual ID, depends on the output type.
|
|
- **%I** an ID defined by the user for this output.
|
|
- **%p** pcb/sch title from pcb metadata.
|
|
- **%r** revision from pcb/sch metadata.
|
|
- **%T** time the script was started.
|
|
- **%x** a suitable extension for the output type.
|
|
- **%v** the `file_id` of the current variant, or the global variant if outside a variant scope.
|
|
- **%V** the `name` of the current variant, or the global variant if outside a variant scope.
|
|
|
|
They are compatible with the ones used by IBoM.
|
|
The default value for `global.output` is `%f-%i.%x`.
|
|
If you want to include the revision you could add the following definition:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
global:
|
|
output: '%f_rev_%r-%i.%x'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Note that the following patterns: **%c**, **%C`n`**, **%d**, **%f**, **%F**, **%p** and **%r** depends on the context.
|
|
If you use them for an output related to the PCB these values will be obtained from the PCB.
|
|
If you need to force the origin of the data you can use **%bX** for the PCB and **%sX** for the schematic, where
|
|
**X** is the pattern to expand.
|
|
|
|
#### Default *dir* option
|
|
|
|
The default `dir` value for any output is `.`. You can change it here.
|
|
|
|
Expansion patterns are allowed.
|
|
|
|
Note that you can use this value as a base for output's `dir` options. In this case the value defined in the `output` must start with `+`.
|
|
In this case the `+` is replaced by the default `dir` value defined here.
|
|
|
|
#### Default *variant* option
|
|
|
|
This option controls the default variant applied to all the outputs. Example:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
global:
|
|
variant: 'production'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### Default *units* option
|
|
|
|
This option controls the default value for the `position` and `bom` outputs.
|
|
If you don't define it then the internal defaults of each output are applied. But when you define it the default is the defined value.
|
|
|
|
On KiCad 6 the dimensions has units. When you create a new dimension it uses *automatic* units. This means that KiCad uses the units currently selected.
|
|
This selection isn't stored in the PCB file. The global `units` value is used by KiBot instead.
|
|
|
|
#### Output directory option
|
|
|
|
The `out_dir` option can define the base output directory. This is the same as the `-d`/`--out-dir` command line option.
|
|
Note that the command line option has precedence over it.
|
|
|
|
Expansion patterns are applied to this value, but you should avoid using patterns that expand according to the context, i.e. **%c**, **%d**, **%f**, **%F**, **%p** and **%r**.
|
|
The behavior of these patterns isn't fully defined in this case and the results may change in the future.
|
|
|
|
#### Date format option
|
|
|
|
* The **%d**, **%sd** and **%bd** patterns use the date and time from the PCB and schematic.
|
|
When abscent they use the file timestamp, and the `date_time_format` global option controls the format used.
|
|
When available, and in ISO format, the `date_format` controls the format used.
|
|
You can disable this reformatting assigning `false` to the `date_reformat` option.
|
|
* The **%D** format is controlled by the `date_format` global option.
|
|
* The **%T** format is controlled by the `time_format` global option.
|
|
|
|
In all cases the format is the one used by the `strftime` POSIX function, for more information visit this [site](https://strftime.org/).
|
|
|
|
#### PCB details options
|
|
|
|
The following variables control the default colors and they are used for documentation purposes:
|
|
|
|
- `pcb_material` [FR4] PCB core material.
|
|
Currently known are FR1 to FR5
|
|
- `solder_mask_color` [green] Color for the solder mask.
|
|
Currently known are green, black, white, yellow, purple, blue and red.
|
|
- `silk_screen_color` [white] Color for the markings.
|
|
Currently known are black and white.
|
|
- `pcb_finish` [HAL] Finishing used to protect pads.
|
|
Currently known are None, HAL, HASL, ENIG and ImAg.
|
|
|
|
#### Filtering KiBot warnings
|
|
|
|
KiBot warnings are marked with `(Wn)` where *n* is the warning id.
|
|
|
|
Some warnings are just recommendations and you could want to avoid them to focus on details that are more relevant to your project.
|
|
In this case you can define filters in a similar way used to [filter DRC/ERC errors](#filtering-drc-and-erc-errors).
|
|
|
|
As an example, if you have the following warning:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
WARNING:(W43) Missing component `l1:FooBar`
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
You can create the following filter to remove it:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
global:
|
|
filters:
|
|
- number: 43
|
|
regex: 'FooBar'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### All available global options
|
|
|
|
global:
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `aliases_for_3d_models`: [list(dict)] List of aliases for the 3D models (KiCad 6).
|
|
KiCad stores 3D aliases with the user settings, not locally.
|
|
This makes impossible to create self contained projects.
|
|
You can define aliases here to workaround this problem.
|
|
The values defined here has precedence over the KiCad configuration.
|
|
Related to https://gitlab.com/kicad/code/kicad/-/issues/3792.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- *alias*: Alias for name.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Name of the alias.
|
|
- *text*: Alias for value.
|
|
- `value`: [string=''] Path to the 3D model.
|
|
- *variable*: Alias for name.
|
|
- `castellated_pads`: [boolean=false] Has the PCB castelletad pads?
|
|
KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Board Finish -> Has castellated pads.
|
|
- *copper_finish*: Alias for pcb_finish.
|
|
- `copper_thickness`: [number|string] Copper thickness in micrometers (1 Oz is 35 micrometers).
|
|
KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Physical Stackup.
|
|
- `cross_footprints_for_dnp`: [boolean=true] Draw a cross for excluded components in the `Fab` layer.
|
|
- `cross_no_body`: [boolean=false] Cross components even when they don't have a body. Only for KiCad 6.
|
|
- `csv_accept_no_ref`: [boolean=false] Accept aggregating CSV files without references (Experimental).
|
|
- `date_format`: [string='%Y-%m-%d'] Format used for the day we started the script.
|
|
Is also used for the PCB/SCH date formatting when `time_reformat` is enabled (default behavior).
|
|
Uses the `strftime` format.
|
|
- `date_time_format`: [string='%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S'] Format used for the PCB and schematic date when using the file timestamp. Uses the `strftime` format.
|
|
- `dir`: [string=''] Default pattern for the output directories. It also applies to the preflights, unless
|
|
`use_dir_for_preflights` is disabled.
|
|
- `disable_3d_alias_as_env`: [boolean=false] Disable the use of environment and text variables as 3D models aliases.
|
|
- `drc_exclusions_workaround`: [boolean=false] KiCad 6 introduced DRC exclusions. They are stored in the project but ignored by the Python API.
|
|
This is reported as bug number 11562 (https://gitlab.com/kicad/code/kicad/-/issues/11562).
|
|
If you really need exclusions enable this option, this will use the GUI version of the DRC (slower).
|
|
Current KiCad version is 6.0.7 and the bug is still there.
|
|
- `drill_size_increment`: [number=0.05] This is the difference between drill tools in millimeters.
|
|
A manufacturer with 0.05 of increment has drills for 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.25, etc..
|
|
- `edge_connector`: [string='no'] [yes,no,bevelled] Has the PCB edge connectors?
|
|
KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Board Finish -> Edge card connectors.
|
|
- `edge_plating`: [boolean=false] Has the PCB a plated board edge?
|
|
KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Board Finish -> Plated board edge.
|
|
- `environment`: [dict] Used to define environment variables used by KiCad.
|
|
The values defined here are exported as environment variables and has
|
|
more precedence than KiCad paths defined in the GUI.
|
|
You can make reference to any OS environment variable using ${VARIABLE}.
|
|
The KIPRJMOD is also available for expansion.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `define_old`: [boolean=false] Also define legacy versions of the variables.
|
|
Useful when using KiCad 6 and some libs uses old KiCad 5 names.
|
|
- `footprints`: [string=''] System level footprints (aka modules) dir. KiCad 5: KICAD_FOOTPRINT_DIR and KISYSMOD.
|
|
KiCad 6: KICAD6_FOOTPRINT_DIR.
|
|
- `models_3d`: [string=''] System level 3D models dir. KiCad 5: KISYS3DMOD. KiCad 6: KICAD6_3DMODEL_DIR.
|
|
- `symbols`: [string=''] System level symbols dir. KiCad 5: KICAD_SYMBOL_DIR. KiCad 6: KICAD6_SYMBOL_DIR.
|
|
- `templates`: [string=''] System level templates dir. KiCad 5: KICAD_TEMPLATE_DIR. KiCad 6: KICAD6_TEMPLATE_DIR.
|
|
- `third_party`: [string=''] 3rd party dir. KiCad 6: KICAD6_3RD_PARTY.
|
|
- `user_templates`: [string=''] User level templates dir. KiCad 5/6: KICAD_USER_TEMPLATE_DIR.
|
|
- `extra_pth_drill`: [number=0.1] How many millimeters the manufacturer will add to plated holes.
|
|
This is because the plating reduces the hole, so you need to use a bigger drill.
|
|
For more information consult: https://www.eurocircuits.com/pcb-design-guidelines/drilled-holes/.
|
|
- `field_3D_model`: [string='_3D_model'] Name for the field controlling the 3D models used for a component.
|
|
- `filters`: [list(dict)] KiBot warnings to be ignored.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `error`: [string=''] Error id we want to exclude.
|
|
- *error_number*: Alias for number.
|
|
- `filter`: [string=''] Name for the filter, for documentation purposes.
|
|
- *filter_msg*: Alias for filter.
|
|
- `number`: [number=0] Error number we want to exclude.
|
|
- `regex`: [string=''] Regular expression to match the text for the error we want to exclude.
|
|
- *regexp*: Alias for regex.
|
|
- `hide_excluded`: [boolean=false] Default value for the `hide_excluded` option of various PCB outputs.
|
|
- `impedance_controlled`: [boolean=false] The PCB needs specific dielectric characteristics.
|
|
KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Physical Stackup.
|
|
- `kiauto_time_out_scale`: [number=0.0] Time-out multiplier for KiAuto operations.
|
|
- `kiauto_wait_start`: [number=0] Time to wait for KiCad in KiAuto operations.
|
|
- `out_dir`: [string=''] Base output dir, same as command line `--out-dir`.
|
|
- `output`: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Default pattern for output file names. Affected by global options.
|
|
- `pcb_finish`: [string='HAL'] Finishing used to protect pads. Currently used for documentation and to choose default colors.
|
|
KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Board Finish -> Copper Finish option.
|
|
Currently known are None, HAL, HASL, HAL SnPb, HAL lead-free, ENIG, ENEPIG, Hard gold, ImAg, Immersion Silver,
|
|
Immersion Ag, ImAu, Immersion Gold, Immersion Au, Immersion Tin, Immersion Nickel, OSP and HT_OSP.
|
|
- `pcb_material`: [string='FR4'] PCB core material. Currently used for documentation and to choose default colors.
|
|
Currently known are FR1 to FR5.
|
|
- `remove_adhesive_for_dnp`: [boolean=true] When applying filters and variants remove the adhesive (glue) for components that won't be included.
|
|
- `remove_solder_paste_for_dnp`: [boolean=true] When applying filters and variants remove the solder paste for components that won't be included.
|
|
- `restore_project`: [boolean=false] Restore the KiCad project after execution.
|
|
Note that this option will undo operations like `set_text_variables`.
|
|
- `set_text_variables_before_output`: [boolean=false] Run the `set_text_variables` preflight before running each output that involves variants.
|
|
This can be used when a text variable uses the variant and you want to create more than
|
|
one variant in the same run. Note that this could be slow because it forces a board
|
|
reload each time you run an output that uses variants.
|
|
- `silk_screen_color`: [string='white'] Color for the markings. Currently used for documentation and to choose default colors.
|
|
KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Physical Stackup.
|
|
Currently known are black and white.
|
|
- `silk_screen_color_bottom`: [string=''] Color for the bottom silk screen. When not defined `silk_screen_color` is used.
|
|
Read `silk_screen_color` help.
|
|
- `silk_screen_color_top`: [string=''] Color for the top silk screen. When not defined `silk_screen_color` is used.
|
|
Read `silk_screen_color` help.
|
|
- `solder_mask_color`: [string='green'] Color for the solder mask. Currently used for documentation and to choose default colors.
|
|
KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Physical Stackup.
|
|
Currently known are green, black, white, yellow, purple, blue and red.
|
|
- `solder_mask_color_bottom`: [string=''] Color for the bottom solder mask. When not defined `solder_mask_color` is used.
|
|
Read `solder_mask_color` help.
|
|
- `solder_mask_color_top`: [string=''] Color for the top solder mask. When not defined `solder_mask_color` is used.
|
|
Read `solder_mask_color` help.
|
|
- `time_format`: [string='%H-%M-%S'] Format used for the time we started the script. Uses the `strftime` format.
|
|
- `time_reformat`: [boolean=true] Tries to reformat the PCB/SCH date using the `date_format`.
|
|
This assumes you let KiCad fill this value and hence the time is in ISO format (YY-MM-DD).
|
|
- `units`: [string=''] [millimeters,inches,mils] Default units. Affects `position` and `bom` outputs. Also KiCad 6 dimensions.
|
|
- `use_dir_for_preflights`: [boolean=true] Use the global `dir` as subdir for the preflights.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Default variant to apply to all outputs.
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Filters and variants
|
|
|
|
The filters and variants are mechanisms used to modify the circuit components.
|
|
Both concepts are closely related. In fact variants can use filters.
|
|
|
|
The current implementation of the filters allow to exclude components from some of the processing stages. The most common use is to exclude them from some output.
|
|
You can also change components fields/properties and also the 3D model.
|
|
|
|
Variants are currently used to create *assembly variants*. This concept is used to manufacture one PCB used for various products.
|
|
You can learn more about KiBot variants on the following [example repo](https://inti-cmnb.github.io/kibot_variants_arduprog/).
|
|
The example is currently using KiCad 6, if you want to see the example files for KiCad 5 go [here](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kibot_variants_arduprog/tree/KiCad5/).
|
|
|
|
As mentioned above the current use of filters is to mark some components. Mainly to exclude them, but also to mark them as special.
|
|
This is the case of *do not change* components in the BoM.
|
|
|
|
Filters and variants are defined in separated sections. A filter section looks like this:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
filters:
|
|
- name: 'a_short_name'
|
|
type: 'generic'
|
|
comment: 'A description'
|
|
# Filter options
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### Supported filters:
|
|
|
|
- expand_text_vars: Expand_Text_Vars
|
|
This filter expands KiCad 6 text variables (${VARIABLE}).
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `include_kicad_env`: [boolean=true] Also expand KiCad environment variables.
|
|
- `include_os_env`: [boolean=false] Also expand system environment variables.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.
|
|
- field_modify: Field_Modify
|
|
Changes the content of one or more fields.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `fields`: [string|list(string)='Datasheet'] Fields to convert.
|
|
- `include`: [string|list(string)=''] Name of the filter to select which components will be affected.
|
|
Applied to all if nothing specified here.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.
|
|
- `regex`: [string='(https?://\S+)'] Regular expression to match the field content.
|
|
Only fields that matches will be modified.
|
|
An empty regex will match anything.
|
|
The example matches an HTTP URL.
|
|
- `replace`: [string='<a href="\1">\1</a>'] Text to replace, can contain references to sub-expressions.
|
|
The example converts an HTTP URL into an HTML link, like the URLify filter.
|
|
- field_rename: Field_Rename
|
|
This filter implements a field renamer.
|
|
The internal `_kicost_rename` filter emulates the KiCost behavior.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.
|
|
- `rename`: [list(dict)] Fields to rename.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `field`: [string=''] Name of the field to rename.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] New name.
|
|
- generic: Generic filter
|
|
This filter is based on regular expressions.
|
|
It also provides some shortcuts for common situations.
|
|
Note that matches aren't case sensitive and spaces at the beginning and the end are removed.
|
|
The internal `_mechanical` filter emulates the KiBoM behavior for default exclusions.
|
|
The internal `_kicost_dnp` filter emulates KiCost's `dnp` field.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `config_field`: [string='Config'] Name of the field used to classify components.
|
|
- `config_separators`: [string=' ,'] Characters used to separate options inside the config field.
|
|
- `exclude_all_hash_ref`: [boolean=false] Exclude all components with a reference starting with #.
|
|
- `exclude_any`: [list(dict)] A series of regular expressions used to exclude parts.
|
|
If a component matches ANY of these, it will be excluded.
|
|
Column names are case-insensitive.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `column`: [string=''] Name of the column to apply the regular expression.
|
|
- *field*: Alias for column.
|
|
- `invert`: [boolean=false] Invert the regex match result.
|
|
- `match_if_field`: [boolean=false] Match if the field exists, no regex applied. Not affected by `invert`.
|
|
- `match_if_no_field`: [boolean=false] Match if the field doesn't exists, no regex applied. Not affected by `invert`.
|
|
- `regex`: [string=''] Regular expression to match.
|
|
- *regexp*: Alias for regex.
|
|
- `skip_if_no_field`: [boolean=false] Skip this test if the field doesn't exist.
|
|
- `exclude_config`: [boolean=false] Exclude components containing a key value in the config field.
|
|
Separators are applied.
|
|
- `exclude_empty_val`: [boolean=false] Exclude components with empty 'Value'.
|
|
- `exclude_field`: [boolean=false] Exclude components if a field is named as any of the keys.
|
|
- `exclude_refs`: [list(string)] List of references to be excluded.
|
|
Use R* for all references with R prefix.
|
|
- `exclude_smd`: [boolean=false] KiCad 5: exclude components marked as smd in the PCB.
|
|
- `exclude_tht`: [boolean=false] KiCad 5: exclude components marked as through-hole in the PCB.
|
|
- `exclude_value`: [boolean=false] Exclude components if their 'Value' is any of the keys.
|
|
- `exclude_virtual`: [boolean=false] KiCad 5: exclude components marked as virtual in the PCB.
|
|
- `include_only`: [list(dict)] A series of regular expressions used to include parts.
|
|
If there are any regex defined here, only components that match against ANY of them will be included.
|
|
Column/field names are case-insensitive.
|
|
If empty this rule is ignored.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `column`: [string=''] Name of the column to apply the regular expression.
|
|
- *field*: Alias for column.
|
|
- `invert`: [boolean=false] Invert the regex match result.
|
|
- `match_if_field`: [boolean=false] Match if the field exists, no regex applied. Not affected by `invert`.
|
|
- `match_if_no_field`: [boolean=false] Match if the field doesn't exists, no regex applied. Not affected by `invert`.
|
|
- `regex`: [string=''] Regular expression to match.
|
|
- *regexp*: Alias for regex.
|
|
- `skip_if_no_field`: [boolean=false] Skip this test if the field doesn't exist.
|
|
- `invert`: [boolean=false] Invert the result of the filter.
|
|
- `keys`: [string|list(string)=dnf_list] [dnc_list,dnf_list] List of keys to match.
|
|
The `dnf_list` and `dnc_list` internal lists can be specified as strings.
|
|
Use `dnf_list` for ['dnf', 'dnl', 'dnp', 'do not fit', 'do not load', 'do not place', 'no stuff', 'nofit', 'noload', 'noplace', 'nostuff', 'not fitted', 'not loaded', 'not placed'].
|
|
Use `dnc_list` for ['dnc', 'do not change', 'fixed', 'no change'].
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.
|
|
- rot_footprint: Rot_Footprint
|
|
This filter can rotate footprints, used for the positions file generation.
|
|
Some manufacturers use a different rotation than KiCad.
|
|
The internal `_rot_footprint` filter implements the simplest case.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `extend`: [boolean=true] Extends the internal list of rotations with the one provided.
|
|
Otherwise just use the provided list.
|
|
- `invert_bottom`: [boolean=false] Rotation for bottom components is negated, resulting in either: `(- component rot - angle)`
|
|
or when combined with `negative_bottom`, `(angle - component rot)`.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.
|
|
- `negative_bottom`: [boolean=true] Rotation for bottom components is computed via subtraction as `(component rot - angle)`.
|
|
- `rotations`: [list(list(string))] A list of pairs regular expression/rotation.
|
|
Components matching the regular expression will be rotated the indicated angle.
|
|
- `skip_bottom`: [boolean=false] Do not rotate components on the bottom.
|
|
- `skip_top`: [boolean=false] Do not rotate components on the top.
|
|
- subparts: Subparts
|
|
This filter implements the KiCost subparts mechanism.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `check_multiplier`: [list(string)] List of fields to include for multiplier computation.
|
|
If empty all fields in `split_fields` and `manf_pn_field` are used.
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `manf_field`: [string='manf'] Field for the manufacturer name.
|
|
- `manf_pn_field`: [string='manf#'] Field for the manufacturer part number.
|
|
- `modify_first_value`: [boolean=true] Modify even the value for the first component in the list (KiCost behavior).
|
|
- `modify_value`: [boolean=true] Add '- p N/M' to the value.
|
|
- `mult_separators`: [string=':'] Separators used for the multiplier. Each character in this string is a valid separator.
|
|
- `multiplier`: [boolean=true] Enables the subpart multiplier mechanism.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.
|
|
- `ref_sep`: [string='#'] Separator used in the reference (i.e. R10#1).
|
|
- `separators`: [string=';,'] Separators used between subparts. Each character in this string is a valid separator.
|
|
- `split_fields`: [list(string)] List of fields to split, usually the distributors part numbers.
|
|
- `split_fields_expand`: [boolean=false] When `true` the fields in `split_fields` are added to the internal names.
|
|
- `use_ref_sep_for_first`: [boolean=true] Force the reference separator use even for the first component in the list (KiCost behavior).
|
|
- `value_alt_field`: [string='value_subparts'] Field containing replacements for the `Value` field. So we get real values for split parts.
|
|
- urlify: URLify
|
|
Converts URL text in fields to HTML URLs.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `fields`: [string|list(string)='Datasheet'] Fields to convert.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.
|
|
- var_rename: Var_Rename
|
|
This filter implements the VARIANT:FIELD=VALUE renamer to get FIELD=VALUE when VARIANT is in use.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `force_variant`: [string=''] Use this variant instead of the current variant. Useful for IBoM variants.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.
|
|
- `separator`: [string=':'] Separator used between the variant and the field name.
|
|
- `variant_to_value`: [boolean=false] Rename fields matching the variant to the value of the component.
|
|
- var_rename_kicost: Var_Rename_KiCost
|
|
This filter implements the kicost.VARIANT:FIELD=VALUE renamer to get FIELD=VALUE when VARIANT is in use.
|
|
It applies the KiCost concept of variants (a regex to match the VARIANT).
|
|
The internal `_var_rename_kicost` filter emulates the KiCost behavior.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.
|
|
- `prefix`: [string='kicost.'] A mandatory prefix. Is not case sensitive.
|
|
- `separator`: [string=':'] Separator used between the variant and the field name.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Variant regex to match the VARIANT part.
|
|
When empty the currently selected variant is used.
|
|
- `variant_to_value`: [boolean=false] Rename fields matching the variant to the value of the component.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Examples for filters
|
|
|
|
The [tests/yaml_samples](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/tree/master/tests/yaml_samples) directory contains all the regression tests. Many of them test the filters functionality.
|
|
|
|
- [int_bom_exclude_any.kibot.yaml](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/tree/master/tests/yaml_samples/int_bom_exclude_any.kibot.yaml): Shows how to use regular expressions to match fields and exclude components. Is the more powerful filter mechanism.
|
|
- [int_bom_fil_1.kibot.yaml](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/tree/master/tests/yaml_samples/int_bom_fil_1.kibot.yaml): Shows various mechanisms. In particular how to change the list of keywords, usually used to match 'DNF', meaning you can exclude components with arbitrary text.
|
|
- [int_bom_fil_2.kibot.yaml](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/tree/master/tests/yaml_samples/int_bom_fil_2.kibot.yaml): Shows how to use KiCad 5 module attributes (from the PCB) to filter SMD, THT and Virtual components. Note KiCad 6 is redefining the attributes.
|
|
- [int_bom_include_only.kibot.yaml](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/tree/master/tests/yaml_samples/int_bom_include_only.kibot.yaml): Shows how to use regular expressions to match only some components, instead of including a few.
|
|
- [int_bom_var_t2is_csv.kibot.yaml](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/tree/master/tests/yaml_samples/int_bom_var_t2is_csv.kibot.yaml): Shows how to use filters and variants simultaneously, not a good idea, but possible.
|
|
- [print_pdf_no_inductors_1.kibot.yaml](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/tree/master/tests/yaml_samples/print_pdf_no_inductors_1.kibot.yaml): Shows how to change the `dnf_filter` for a KiBoM variant.
|
|
- [print_pdf_no_inductors_2.kibot.yaml](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/tree/master/tests/yaml_samples/print_pdf_no_inductors_2.kibot.yaml): Shows how to do what `print_pdf_no_inductors_1.kibot.yaml` does but without the need of a variant.
|
|
|
|
#### Built-in filters
|
|
|
|
- **_datasheet_link** converts Datasheet fields containing URLs into HTML links
|
|
- **_expand_text_vars** is a default `expand_text_vars` filter
|
|
- **_kibom_dnc_Config** it uses the internal `dnc_list` to exclude components with
|
|
- Value matching any of the keys
|
|
- Any of the keys in the `Config` field (comma or space separated)
|
|
- **_kibom_dnf_Config** it uses the internal `dnf_list` to exclude components with
|
|
- Value matching any of the keys
|
|
- Any of the keys in the `Config` field (comma or space separated)
|
|
- **_kicost_dnp** used emulate the way KiCost handles the `dnp` field.
|
|
- If the field is 0 the component is included, otherwise excluded.
|
|
- **_kicost_rename** is a `field_rename` filter that applies KiCost renamings.
|
|
- Includes all `manf#` and `manf` variations supported by KiCost
|
|
- Includes all distributor part number variations supported by KiCost
|
|
- 'version' -> 'variant'
|
|
- 'nopop' -> 'dnp'
|
|
- 'description' -> 'desc'
|
|
- 'pdf' -> 'datasheet'
|
|
- **_mechanical** is used to exclude:
|
|
- References that start with #
|
|
- Virtual components
|
|
- References that match: '^TP[0-9]*' or '^FID'
|
|
- Part names that match: 'regex': 'mount.*hole' or 'solder.*bridge' or 'solder.*jump' or 'test.*point'
|
|
- Footprints that match: 'test.*point' or 'mount.*hole' or 'fiducial'
|
|
- **_rot_footprint** is a default `rot_footprint` filter
|
|
- **_var_rename** is a default `var_rename` filter
|
|
- **_var_rename_kicost** is a default `var_rename_kicost` filter
|
|
|
|
Note that the **_kibom_...** filters uses a field named `Config`, but you can customise them invoking **_kibom_dnf_FIELD**. This will create an equivalent filter, but using the indicated **FIELD**.
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Supported variants:
|
|
|
|
- `ibom`: IBoM variant style
|
|
The Config field (configurable) contains a value.
|
|
If this value matches with a value in the whitelist is included.
|
|
If this value matches with a value in the blacklist is excluded.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `dnc_filter`: [string|list(string)=''] Name of the filter to mark components as 'Do Not Change'.
|
|
Use '_kibom_dnc' for the default KiBoM behavior.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)=''] Name of the filter to mark components as 'Do Not Fit'.
|
|
Use '_kibom_dnf' for the default KiBoM behavior.
|
|
Use '_kicost_dnp'' for the default KiCost behavior.
|
|
- `exclude_filter`: [string|list(string)=''] Name of the filter to exclude components from BoM processing.
|
|
Use '_mechanical' for the default KiBoM behavior.
|
|
- `file_id`: [string=''] Text to use as the replacement for %v expansion.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Used to identify this particular variant definition.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)=''] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
Use '_var_rename' to transform VARIANT:FIELD fields.
|
|
Use '_var_rename_kicost' to transform kicost.VARIANT:FIELD fields.
|
|
Use '_kicost_rename' to apply KiCost field rename rules.
|
|
- `variant_field`: [string='Config'] Name of the field that stores board variant for component.
|
|
- `variants_blacklist`: [string|list(string)=''] List of board variants to exclude from the BOM.
|
|
- `variants_whitelist`: [string|list(string)=''] List of board variants to include in the BOM.
|
|
- `kibom`: KiBoM variant style
|
|
The Config field (configurable) contains a comma separated list of variant directives.
|
|
-VARIANT excludes a component from VARIANT.
|
|
+VARIANT includes the component only if we are using this variant.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `config_field`: [string='Config'] Name of the field used to classify components.
|
|
- `dnc_filter`: [string|list(string)='_kibom_dnc_CONFIG_FIELD'] Name of the filter to mark components as 'Do Not Change'.
|
|
Use '_kibom_dnc' for the default KiBoM behavior.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_kibom_dnf_CONFIG_FIELD'] Name of the filter to mark components as 'Do Not Fit'.
|
|
Use '_kibom_dnf' for the default KiBoM behavior.
|
|
Use '_kicost_dnp'_kibom_dnf_CONFIG_FIELD' for the default KiCost behavior.
|
|
- `exclude_filter`: [string|list(string)='_mechanical'] Name of the filter to exclude components from BoM processing.
|
|
Use '_mechanical' for the default KiBoM behavior.
|
|
- `file_id`: [string=''] Text to use as the replacement for %v expansion.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Used to identify this particular variant definition.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)=''] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
Use '_var_rename' to transform VARIANT:FIELD fields.
|
|
Use '_var_rename_kicost' to transform kicost.VARIANT:FIELD fields.
|
|
Use '_kicost_rename' to apply KiCost field rename rules.
|
|
- `variant`: [string|list(string)=''] Board variant(s).
|
|
- `kicost`: KiCost variant style
|
|
The `variant` field (configurable) contains one or more values.
|
|
If any of these values matches the variant regex the component is included.
|
|
By default a pre-transform filter is applied to support kicost.VARIANT:FIELD and
|
|
field name aliases used by KiCost.
|
|
Also a default `dnf_filter` implements the KiCost DNP mechanism.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `dnc_filter`: [string|list(string)=''] Name of the filter to mark components as 'Do Not Change'.
|
|
Use '_kibom_dnc' for the default KiBoM behavior.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)=''] Name of the filter to mark components as 'Do Not Fit'.
|
|
Use '_kibom_dnf' for the default KiBoM behavior.
|
|
Use '_kicost_dnp'' for the default KiCost behavior.
|
|
- `exclude_filter`: [string|list(string)=''] Name of the filter to exclude components from BoM processing.
|
|
Use '_mechanical' for the default KiBoM behavior.
|
|
- `file_id`: [string=''] Text to use as the replacement for %v expansion.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Used to identify this particular variant definition.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)=''] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
Use '_var_rename' to transform VARIANT:FIELD fields.
|
|
Use '_var_rename_kicost' to transform kicost.VARIANT:FIELD fields.
|
|
Use '_kicost_rename' to apply KiCost field rename rules.
|
|
- `separators`: [string=',;/ '] Valid separators for variants in the variant field.
|
|
Each character is a valid separator.
|
|
Only supported internally, don't use it if you plan to use KiCost.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Variants to match (regex).
|
|
- `variant_field`: [string='variant'] Name of the field that stores board variant/s for component.
|
|
Only supported internally, don't use it if you plan to use KiCost.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Changing the 3D model, simple mechanism
|
|
|
|
This mechanism allows small changes to the 3D model. Is simple to use, but the information is located in the schematic.
|
|
|
|
If a component defines the field `_3D_model` then its value will replace the 3D model.
|
|
You can use `var_rename` or `var_rename_kicost` filter to define this field only for certain variants.
|
|
In this way you can change the 3D model according to the component variant.
|
|
|
|
When the component has more than one 3D model you must provide a comma separated list of models to replace the current models.
|
|
|
|
#### Changing the 3D model, complex mechanism
|
|
|
|
When the a component has a long list of 3D models and you want to keep all the information in the PCB you can use this mechanism.
|
|
|
|
The information is stored in the `Text items` of the footprint. If you want to change the 3D models for certain variant you must add an item containing:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
%VARIANT_NAME:SLOT1,SLOT2,SLOTN%
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Where `VARIANT_NAME` is the name of the variant that will change the list of 3D models.
|
|
The `SLOT1,SLOT2,SLOTN` is a comma separated list of 3D model positions in the list of 3D models.
|
|
All the slots listed will be enabled, the rest will be disabled.
|
|
|
|
Here is an [example](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/tree/master/docs/samples/3D_Model_LCD).
|
|
In this example we have a display whose aspect and connectio can radically change according to the variant.
|
|
We have two variants:
|
|
|
|
- `left`, uses a ERM1602DNS-2.1 with a connector on the left and two other pins on the right
|
|
- `top`, uses a WH1602B-TMI-JT# with a single connector on the top
|
|
|
|
We have the following list of 3D models:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_2x07_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
|
|
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_1x16_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
|
|
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_1x01_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
|
|
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_1x01_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
|
|
${KIPRJMOD}/steps/WH1602B-TMI-JT#.step
|
|
${KIPRJMOD}/steps/ERM1602DNS-2.1.step
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The ERM1602DNS-2.1 uses slots 1, 3, 4 and 6. So the effective list will be:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_2x07_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
|
|
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_1x01_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
|
|
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_1x01_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
|
|
${KIPRJMOD}/steps/ERM1602DNS-2.1.step
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The WH1602B-TMI-JT# uses slots 2 and 5. So the effective list will be:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_1x16_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
|
|
${KIPRJMOD}/steps/WH1602B-TMI-JT#.step
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
To achieve it we define the following texts in the footprint: `%left:1,3,4,6%` and `%top:2,5%`.
|
|
Here are both variants:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If you preffer to use the variant specific matching mechanism you can use the following syntax:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
$TEXT_TO_MATCH:SLOT1,SLOT2,SLOTN$
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
In this case the variant will be applied to the `TEXT_TO_MATCH`, if it matches (equivalent to a component fitted) the `SLOT` will be used.
|
|
|
|
Some important notes:
|
|
- If you want to control what models are used when no variant is used you'll need to create a `default` variant.
|
|
This is what the above example does. In this case the `default` variant shows all the connectors, but no display.
|
|
Note that changing the 3D model needs the variants infrastructure.
|
|
- If you are using variants and a lot of them select the same slots you can add a special text: `%_default_:SLOTS%`.
|
|
This will be used if none %VARIANT_NAME:SLOT%` matched.
|
|
- If you want to disable a model and avoid any kind of warning add `_Disabled_by_KiBot` to the 3D model path.
|
|
This could be needed if you want to remove some model and you don't want to adjust the slot numbers.
|
|
- This mechanism can be used with any of the available variants. For this reason we use the `VARIANT_NAME` and we
|
|
avoid relying on any variant specific mechanism. But you can use the alternative syntax if you preffer the variant
|
|
specific matching system.
|
|
|
|
#### DNF and DNC internal keys
|
|
|
|
The current list of **DNF** keys is:
|
|
- dnf
|
|
- dnl
|
|
- dnp
|
|
- do not fit
|
|
- do not place
|
|
- do not load
|
|
- nofit
|
|
- nostuff
|
|
- noplace
|
|
- noload
|
|
- not fitted
|
|
- not loaded
|
|
- not placed
|
|
- no stuff
|
|
|
|
The current list of **DNC** keys is:
|
|
- dnc
|
|
- do not change
|
|
- no change
|
|
- fixed
|
|
|
|
You can define your own lists as the `int_bom_fil_1.kibot.yaml` shows.
|
|
|
|
|
|
### The *outputs* section
|
|
|
|
In this section you put all the things that you want to generate.
|
|
This section contains one or more **outputs**.
|
|
Each output contain the following data:
|
|
|
|
- `name` a name so you can easily identify it.
|
|
- `comment` a short description of this output.
|
|
- `type` selects which type of output will be generated.
|
|
Examples are *gerbers*, *drill files* and *pick & place files*
|
|
- `dir` is the directory where this output will be stored.
|
|
- `extends` used to use another output's `options` as base.
|
|
- `run_by_default` indicates this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default` can be used to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
- `output_id` text to use for the %I expansion content.
|
|
- `options` contains one or more options to configure this output.
|
|
- `layers` a list of layers used for this output. Not all outputs needs this subsection.
|
|
|
|
**Important note about the layers**: In the original [kiplot](https://github.com/johnbeard/kiplot)
|
|
(from [John Beard](https://github.com/johnbeard)) the name of the inner layers was *Inner.N* where
|
|
*N* is the number of the layer, i.e. *Inner.1* is the first inner layer.
|
|
This format is supported for compatibility.
|
|
Note that this generated a lot of confusion because the default KiCad name for the first inner layer
|
|
is *In1.Cu*.
|
|
People filled issues and submitted pull-requests to fix it, thinking that inner layers weren't supported.
|
|
Currently KiCad allows renaming these layers, so this version of kiplot supports the name used in
|
|
KiCad. Just use the same name you see in the user interface.
|
|
|
|
The available values for *type* are:
|
|
- Plot formats:
|
|
- `gerber` the gerbers for fabrication.
|
|
- `ps` postscript plot
|
|
- `hpgl` format for laser printers
|
|
- `svg` scalable vector graphics
|
|
- `pdf` portable document format
|
|
- `dxf` mechanical CAD format
|
|
- Drill formats:
|
|
- `excellon` data for the drilling machine
|
|
- `gerb_drill` drilling positions in a gerber file
|
|
- Pick & place
|
|
- `position` of the components for the pick & place machine
|
|
- Documentation
|
|
- `pdf_sch_print` schematic in PDF format
|
|
- `svg_sch_print` schematic in SVG format
|
|
- `pdf_pcb_print` PDF file containing one or more layer and the page frame
|
|
- `svg_pcb_print` SVG file containing one or more layer and the page frame
|
|
- `pcb_print` PDF/SVG/PNG/EPS/PS, similar to `pdf_pcb_print` and `svg_pcb_print`, with more flexibility
|
|
- `report` generates a report about the PDF. Can include images from the above outputs.
|
|
- Bill of Materials
|
|
- `bom` The internal BoM generator.
|
|
- `kibom` BoM in HTML or CSV format generated by [KiBoM](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBoM)
|
|
- `ibom` Interactive HTML BoM generated by [InteractiveHtmlBom](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/InteractiveHtmlBom)
|
|
- `kicost` BoM in XLSX format with costs generated by [KiCost](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiCost)
|
|
- 3D model:
|
|
- `step` *Standard for the Exchange of Product Data* for the PCB
|
|
- `render_3d` PCB render, from the KiCad's 3D Viewer (broken in KiCad 6.0.0)
|
|
- Others:
|
|
- `boardview` creates a file useful to repair the board, but without disclosing the full layout.
|
|
- `gencad` exports the PCB in GENCAD format.
|
|
- `compress` creates an archive containing generated data.
|
|
- `download_datasheets` downloads the datasheets for all the components.
|
|
- `pcbdraw` nice images of the PCB in customized colors.
|
|
- `pdfunite` joins various PDF files into one.
|
|
- `qr_lib` generates symbol and footprints for QR codes.
|
|
- `sch_variant` the schematic after applying all filters and variants, including crossed components.
|
|
|
|
Here is an example of a configuration file to generate the gerbers for the top and bottom layers:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
kibot:
|
|
version: 1
|
|
|
|
preflight:
|
|
run_drc: true
|
|
|
|
outputs:
|
|
|
|
- name: 'gerbers'
|
|
comment: "Gerbers for the board house"
|
|
type: gerber
|
|
dir: gerberdir
|
|
options:
|
|
# generic layer options
|
|
exclude_edge_layer: false
|
|
exclude_pads_from_silkscreen: false
|
|
plot_sheet_reference: false
|
|
plot_footprint_refs: true
|
|
plot_footprint_values: true
|
|
force_plot_invisible_refs_vals: false
|
|
tent_vias: true
|
|
line_width: 0.15
|
|
|
|
# gerber options
|
|
use_aux_axis_as_origin: false
|
|
subtract_mask_from_silk: true
|
|
use_protel_extensions: false
|
|
gerber_precision: 4.5
|
|
create_gerber_job_file: true
|
|
use_gerber_x2_attributes: true
|
|
use_gerber_net_attributes: false
|
|
|
|
layers:
|
|
- 'F.Cu'
|
|
- 'B.Cu'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Most options are the same you'll find in the KiCad dialogs.
|
|
|
|
Outputs are generated in the order they are declared in the YAML file.
|
|
To create them in an arbitrary order use the `--cli-order` command line option and they will be created in the order specified in the command line.
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Specifying the layers
|
|
|
|
You have various ways to specify the layers. If you need to specify just one layer you can just use its name:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
layers: 'F.Cu'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If you want to specify all the available layers:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
layers: 'all'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
You can also select the layers you want in KiCad (using File, Plot dialog) and save your PCB.
|
|
Then you just need to use:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
layers: 'selected'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
You can also use any of the following grup of layers:
|
|
|
|
- **copper** all the copper layers
|
|
- **technical** all the technical layers (silk sreen, solder mask, paste, adhesive, etc.)
|
|
- **user** all the user layers (draw, comments, eco, margin, edge cuts, etc.)
|
|
|
|
You can also mix the above definitions using a list:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
layers:
|
|
- 'copper'
|
|
- 'Dwgs.User'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This will select all the copper layers and the user drawings.
|
|
Note that the above mentioned options will use file name suffixes and descriptions selected automatically.
|
|
If you want to use a particular suffix and provide better descriptions you can use the following format:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
layers:
|
|
- layer: 'F.Cu'
|
|
suffix: 'F_Cu'
|
|
description: 'Front copper'
|
|
- layer: 'B.Cu'
|
|
suffix: 'B_Cu'
|
|
description: 'Bottom copper'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
You can also mix the styles:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
layers:
|
|
- 'copper'
|
|
- layer: 'Cmts.User'
|
|
suffix: 'Cmts_User'
|
|
description: 'User comments'
|
|
- 'Dwgs.User'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If you need to use the same list of layers for various outputs you can use YAML anchors.
|
|
The first time you define the list of layers just assign an anchor, here is an example:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
layers: &copper_and_cmts
|
|
- copper
|
|
- 'Cmts.User'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Next time you need this list just use an alias, like this:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
layers: *copper_and_cmts
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### Supported outputs:
|
|
|
|
Notes:
|
|
1. Most relevant options are listed first and in **bold**. Which ones are more relevant is quite arbitrary, comments are welcome.
|
|
2. Aliases are listed in *italics*.
|
|
|
|
* BoardView
|
|
* Type: `boardview`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB in board view format.
|
|
This format allows simple pads and connections navigation, mainly for circuit debug.
|
|
The output can be loaded using Open Board View (https://openboardview.org/)
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `boardview` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=boardview, %x=brd). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* BoM (Bill of Materials)
|
|
* Type: `bom`
|
|
* Description: Used to generate the BoM in CSV, HTML, TSV, TXT, XML or XLSX format using the internal BoM.
|
|
This output can generate XYRS files (pick and place files).
|
|
Is compatible with KiBoM, but doesn't need to update the XML netlist because the components
|
|
are loaded from the schematic.
|
|
Important differences with KiBoM output:
|
|
- All options are in the main `options` section, not in `conf` subsection.
|
|
- The `Component` column is named `Row` and works just like any other column.
|
|
This output is what you get from the 'Tools/Generate Bill of Materials' menu in eeschema.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `bom` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`columns`**: [list(dict)|list(string)] List of columns to display.
|
|
Can be just the name of the field.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`field`**: [string=''] Name of the field to use for this column.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Name to display in the header. The field is used when empty.
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] Used as explanation for this column. The XLSX output uses it.
|
|
- `join`: [list(dict)|list(string)|string=''] List of fields to join to this column.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`field`**: [string=''] Name of the field.
|
|
- `text`: [string=''] Text to use instead of a field. This option is incompatible with the `field` option.
|
|
Any space to separate it should be added in the text.
|
|
Use \n for newline and \t for tab.
|
|
- `text_after`: [string=''] Text to add after the field content. Will be added only if the field isn't empty.
|
|
Any space to separate it should be added in the text.
|
|
Use \n for newline and \t for tab.
|
|
- `text_before`: [string=''] Text to add before the field content. Will be added only if the field isn't empty.
|
|
Any space to separate it should be added in the text.
|
|
Use \n for newline and \t for tab.
|
|
- `level`: [number=0] Used to group columns. The XLSX output uses it to collapse columns.
|
|
- **`csv`**: [dict] Options for the CSV, TXT and TSV formats.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`quote_all`**: [boolean=false] Enclose all values using double quotes.
|
|
- **`separator`**: [string=','] CSV Separator. TXT and TSV always use tab as delimiter.
|
|
- `hide_header`: [boolean=false] Hide the header line (names of the columns).
|
|
- `hide_pcb_info`: [boolean=false] Hide project information.
|
|
- `hide_stats_info`: [boolean=false] Hide statistics information.
|
|
- **`format`**: [string=''] [HTML,CSV,TXT,TSV,XML,XLSX] format for the BoM.
|
|
Defaults to CSV or a guess according to the options..
|
|
- **`group_fields`**: [list(string)] List of fields used for sorting individual components into groups.
|
|
Components which match (comparing *all* fields) will be grouped together.
|
|
Field names are case-insensitive.
|
|
If empty: ['Part', 'Part Lib', 'Value', 'Footprint', 'Footprint Lib',
|
|
'Voltage', 'Tolerance', 'Current', 'Power'] is used.
|
|
- **`html`**: [dict] Options for the HTML format.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`datasheet_as_link`**: [string=''] Column with links to the datasheet.
|
|
- **`generate_dnf`**: [boolean=true] Generate a separated section for DNF (Do Not Fit) components.
|
|
- **`logo`**: [string|boolean=''] PNG file to use as logo, use false to remove.
|
|
- **`title`**: [string='KiBot Bill of Materials'] BoM title.
|
|
- `col_colors`: [boolean=true] Use colors to show the field type.
|
|
- `digikey_link`: [string|list(string)=''] Column/s containing Digi-Key part numbers, will be linked to web page.
|
|
- `extra_info`: [string|list(string)=''] Information to put after the title and before the pcb and stats info.
|
|
- `hide_pcb_info`: [boolean=false] Hide project information.
|
|
- `hide_stats_info`: [boolean=false] Hide statistics information.
|
|
- `highlight_empty`: [boolean=true] Use a color for empty cells. Applies only when `col_colors` is `true`.
|
|
- `style`: [string='modern-blue'] Page style. Internal styles: modern-blue, modern-green, modern-red and classic.
|
|
Or you can provide a CSS file name. Please use .css as file extension..
|
|
- **`ignore_dnf`**: [boolean=true] Exclude DNF (Do Not Fit) components.
|
|
- **`normalize_values`**: [boolean=false] Try to normalize the R, L and C values, producing uniform units and prefixes.
|
|
- **`number`**: [number=1] Number of boards to build (components multiplier).
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] filename for the output (%i=bom). Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`sort_style`**: [string='type_value'] [type_value,type_value_ref,ref] Sorting criteria.
|
|
- **`units`**: [string='millimeters'] [millimeters,inches,mils] Units used for the positions ('Footprint X' and 'Footprint Y' columns).
|
|
Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`xlsx`**: [dict] Options for the XLSX format.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`datasheet_as_link`**: [string=''] Column with links to the datasheet.
|
|
- **`generate_dnf`**: [boolean=true] Generate a separated section for DNF (Do Not Fit) components.
|
|
- **`kicost`**: [boolean=false] Enable KiCost worksheet creation.
|
|
- **`logo`**: [string|boolean=''] PNG file to use as logo, use false to remove.
|
|
- **`specs`**: [boolean=false] Enable Specs worksheet creation. Contains specifications for the components.
|
|
Works with only some KiCost APIs.
|
|
- **`title`**: [string='KiBot Bill of Materials'] BoM title.
|
|
- `col_colors`: [boolean=true] Use colors to show the field type.
|
|
- `digikey_link`: [string|list(string)=''] Column/s containing Digi-Key part numbers, will be linked to web page.
|
|
- `extra_info`: [string|list(string)=''] Information to put after the title and before the pcb and stats info.
|
|
- `hide_pcb_info`: [boolean=false] Hide project information.
|
|
- `hide_stats_info`: [boolean=false] Hide statistics information.
|
|
- `highlight_empty`: [boolean=true] Use a color for empty cells. Applies only when `col_colors` is `true`.
|
|
- `kicost_api_disable`: [string|list(string)=''] List of KiCost APIs to disable.
|
|
- `kicost_api_enable`: [string|list(string)=''] List of KiCost APIs to enable.
|
|
- `kicost_config`: [string=''] KiCost configuration file. It contains the keys for the different distributors APIs.
|
|
The regular KiCost config is used when empty.
|
|
- `kicost_dist_desc`: [boolean=false] Used to add a column with the distributor's description. So you can check this is the right component.
|
|
- `logo_scale`: [number=2] Scaling factor for the logo. Note that this value isn't honored by all spreadsheet software.
|
|
- `max_col_width`: [number=60] [20,999] Maximum column width (characters).
|
|
- `specs_columns`: [list(dict)|list(string)] Which columns are included in the Specs worksheet. Use `References` for the references,
|
|
'Row' for the order and 'Sep' to separate groups at the same level. By default all are included.
|
|
Column names are distributor specific, the following aren't: '_desc', '_value', '_tolerance', '_footprint',
|
|
'_power', '_current', '_voltage', '_frequency', '_temp_coeff', '_manf', '_size'.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`field`**: [string=''] Name of the field to use for this column.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Name to display in the header. The field is used when empty.
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] Used as explanation for this column. The XLSX output uses it.
|
|
- `join`: [list(dict)|list(string)|string=''] List of fields to join to this column.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`field`**: [string=''] Name of the field.
|
|
- `text`: [string=''] Text to use instead of a field. This option is incompatible with the `field` option.
|
|
Any space to separate it should be added in the text.
|
|
Use \n for newline and \t for tab.
|
|
- `text_after`: [string=''] Text to add after the field content. Will be added only if the field isn't empty.
|
|
Any space to separate it should be added in the text.
|
|
Use \n for newline and \t for tab.
|
|
- `text_before`: [string=''] Text to add before the field content. Will be added only if the field isn't empty.
|
|
Any space to separate it should be added in the text.
|
|
Use \n for newline and \t for tab.
|
|
- `level`: [number=0] Used to group columns. The XLSX output uses it to collapse columns.
|
|
- `style`: [string='modern-blue'] Head style: modern-blue, modern-green, modern-red and classic.
|
|
- `aggregate`: [list(dict)] Add components from other projects.
|
|
You can use CSV files, the first row must contain the names of the fields.
|
|
The `Reference` and `Value` are mandatory, in most cases `Part` is also needed.
|
|
The `Part` column should contain the name/type of the component. This is important for
|
|
passive components (R, L, C, etc.). If this information isn't available consider
|
|
configuring the grouping to exclude the `Part`..
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `delimiter`: [string=','] Delimiter used for CSV files.
|
|
- `file`: [string=''] Name of the schematic to aggregate.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Name to identify this source. If empty we use the name of the schematic.
|
|
- `number`: [number=1] Number of boards to build (components multiplier). Use negative to subtract.
|
|
- `ref_id`: [string=''] A prefix to add to all the references from this project.
|
|
- `angle_positive`: [boolean=true] Always use positive values for the footprint rotation.
|
|
- `bottom_negative_x`: [boolean=false] Use negative X coordinates for footprints on bottom layer (for XYRS).
|
|
- `component_aliases`: [list(list(string))] A series of values which are considered to be equivalent for the part name.
|
|
Each entry is a list of equivalen names. Example: ['c', 'c_small', 'cap' ]
|
|
will ensure the equivalent capacitor symbols can be grouped together.
|
|
If empty the following aliases are used:
|
|
- ['r', 'r_small', 'res', 'resistor']
|
|
- ['l', 'l_small', 'inductor']
|
|
- ['c', 'c_small', 'cap', 'capacitor']
|
|
- ['sw', 'switch']
|
|
- ['zener', 'zenersmall']
|
|
- ['d', 'diode', 'd_small'].
|
|
- `cost_extra_columns`: [list(dict)|list(string)] List of columns to add to the global section of the cost.
|
|
Can be just the name of the field.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`field`**: [string=''] Name of the field to use for this column.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Name to display in the header. The field is used when empty.
|
|
- `comment`: [string=''] Used as explanation for this column. The XLSX output uses it.
|
|
- `join`: [list(dict)|list(string)|string=''] List of fields to join to this column.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`field`**: [string=''] Name of the field.
|
|
- `text`: [string=''] Text to use instead of a field. This option is incompatible with the `field` option.
|
|
Any space to separate it should be added in the text.
|
|
Use \n for newline and \t for tab.
|
|
- `text_after`: [string=''] Text to add after the field content. Will be added only if the field isn't empty.
|
|
Any space to separate it should be added in the text.
|
|
Use \n for newline and \t for tab.
|
|
- `text_before`: [string=''] Text to add before the field content. Will be added only if the field isn't empty.
|
|
Any space to separate it should be added in the text.
|
|
Use \n for newline and \t for tab.
|
|
- `level`: [number=0] Used to group columns. The XLSX output uses it to collapse columns.
|
|
- `count_smd_tht`: [boolean=false] Show the stats about how many of the components are SMD/THT. You must provide the PCB.
|
|
- `distributors`: [string|list(string)] Include this distributors list. Default is all the available.
|
|
- `dnc_filter`: [string|list(string)='_kibom_dnc'] Name of the filter to mark components as 'Do Not Change'.
|
|
The default filter marks components with a DNC value or DNC in the Config field.
|
|
This option is for simple cases, consider using a full variant for complex cases.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_kibom_dnf'] Name of the filter to mark components as 'Do Not Fit'.
|
|
The default filter marks components with a DNF value or DNF in the Config field.
|
|
This option is for simple cases, consider using a full variant for complex cases.
|
|
- `exclude_filter`: [string|list(string)='_mechanical'] Name of the filter to exclude components from BoM processing.
|
|
The default filter excludes test points, fiducial marks, mounting holes, etc.
|
|
This option is for simple cases, consider using a full variant for complex cases.
|
|
- `exclude_marked_in_pcb`: [boolean=false] Exclude components marked with *Exclude from BOM* in the PCB.
|
|
This is a KiCad 6 option.
|
|
- `exclude_marked_in_sch`: [boolean=true] Exclude components marked with *Exclude from bill of materials* in the schematic.
|
|
This is a KiCad 6 option.
|
|
- `expand_text_vars`: [boolean=true] Expand KiCad 6 text variables after applying all filters and variants.
|
|
This is done using a **_expand_text_vars** filter.
|
|
If you need to customize the filter, or apply it before, you can disable this option and
|
|
add a custom filter to the filter chain.
|
|
- `fit_field`: [string='Config'] Field name used for internal filters (not for variants).
|
|
- `footprint_populate_values`: [string|list(string)='no,yes'] Values for the `Footprint Populate` column.
|
|
- `footprint_type_values`: [string|list(string)='SMD,THT,VIRTUAL'] Values for the `Footprint Type` column.
|
|
- `group_connectors`: [boolean=true] Connectors with the same footprints will be grouped together, independent of the name of the connector.
|
|
- `group_fields_fallbacks`: [list(string)] List of fields to be used when the fields in `group_fields` are empty.
|
|
The first field in this list is the fallback for the first in `group_fields`, and so on.
|
|
- `int_qtys`: [boolean=true] Component quantities are always expressed as integers. Using the ceil() function.
|
|
- `merge_blank_fields`: [boolean=true] Component groups with blank fields will be merged into the most compatible group, where possible.
|
|
- `merge_both_blank`: [boolean=true] When creating groups two components with empty/missing field will be interpreted as with the same value.
|
|
- `no_conflict`: [list(string)] List of fields where we tolerate conflicts.
|
|
Use it to avoid undesired warnings.
|
|
By default the field indicated in `fit_field`, the field used for variants and
|
|
the field `part` are excluded.
|
|
- `no_distributors`: [string|list(string)] Exclude this distributors list. They are removed after computing `distributors`.
|
|
- `normalize_locale`: [boolean=false] When normalizing values use the locale decimal point.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
This option is for simple cases, consider using a full variant for complex cases.
|
|
- `ref_id`: [string=''] A prefix to add to all the references from this project. Used for multiple projects.
|
|
- `ref_separator`: [string=' '] Separator used for the list of references.
|
|
- `source_by_id`: [boolean=false] Generate the `Source BoM` column using the reference ID instead of the project name.
|
|
- `use_alt`: [boolean=false] Print grouped references in the alternate compressed style eg: R1-R7,R18.
|
|
- `use_aux_axis_as_origin`: [boolean=true] Use the auxiliary axis as origin for coordinates (KiCad default) (for XYRS).
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant, used to determine which components
|
|
are output to the BoM..
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Archiver (files compressor)
|
|
* Type: `compress`
|
|
* Description: Generates a compressed file containing output files.
|
|
This is used to generate groups of files in compressed file format.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `compress` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`files`**: [list(dict)] Which files will be included.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`from_output`**: [string=''] Collect files from the selected output.
|
|
When used the `source` option is ignored.
|
|
- **`source`**: [string='*'] File names to add, wildcards allowed. Use ** for recursive match.
|
|
By default this pattern is applied to the output dir specified with `-d` command line option.
|
|
See the `from_cwd` option.
|
|
- `dest`: [string=''] Destination directory inside the archive, empty means the same of the file.
|
|
- `filter`: [string='.*'] A regular expression that source files must match.
|
|
- `from_cwd`: [boolean=false] Use the current working directory instead of the dir specified by `-d`.
|
|
- **`format`**: [string='ZIP'] [ZIP,TAR,RAR] Output file format.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the generated archive (%i=name of the output %x=according to format). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `compression`: [string='auto'] [auto,stored,deflated,bzip2,lzma] Compression algorithm. Use auto to let KiBot select a suitable one.
|
|
- `follow_links`: [boolean=true] Store the file pointed by symlinks, not the symlink.
|
|
- `move_files`: [boolean=false] Move the files to the archive. In other words: remove the files after adding them to the archive.
|
|
- *remove_files*: Alias for move_files.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=10] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Files copier
|
|
* Type: `copy_files`
|
|
* Description: Used to copy files to the output directory.
|
|
Useful when an external tool is used to compress the output directory.
|
|
Note that you can use the `compress` output to create archives
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `copy_files` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`download`**: [boolean=true] Downloads missing 3D models from KiCad git. Only applies to models in KISYS3DMOD.
|
|
- **`files`**: [list(dict)] Which files will be included.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`source`**: [string='*'] File names to add, wildcards allowed. Use ** for recursive match.
|
|
By default this pattern is applied to the current working dir.
|
|
See the `from_outdir` option.
|
|
- **`source_type`**: [string='files'] [files,out_files,output,3d_models] How to interpret `source`.
|
|
`files`: is a pattern for files relative to the working directory.
|
|
`out_files`: is a pattern for files relative to output dir specified
|
|
with `-d` command line option.
|
|
`output`: is the name of an `output`.
|
|
`3d_models`: is a pattern to match the name of the 3D models extracted
|
|
from the PCB..
|
|
- `dest`: [string=''] Destination directory inside the output dir, empty means the same of the file
|
|
relative to the source directory.
|
|
For the `3d_models` type you can use DIR+ to create subdirs under DIR.
|
|
- `filter`: [string='.*'] A regular expression that source files must match.
|
|
- `save_pcb`: [boolean=false] Only usable for the `3d_models` mode.
|
|
Save a PCB copy modified to use the copied 3D models.
|
|
- **`no_virtual`**: [boolean=false] Used to exclude 3D models for components with 'virtual' attribute.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `follow_links`: [boolean=true] Store the file pointed by symlinks, not the symlink.
|
|
- `kicad_3d_url`: [string='https://gitlab.com/kicad/libraries/kicad-packages3D/-/raw/master/'] Base URL for the KiCad 3D models.
|
|
- `link_no_copy`: [boolean=false] Create symlinks instead of copying files.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=11] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Diff
|
|
* Type: `diff`
|
|
* Description: Generates a PDF with the differences between two PCBs or schematics.
|
|
Recursive git submodules aren't supported (submodules inside submodules)
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`layers`**: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user]
|
|
List of PCB layers to use. When empty all available layers are used.
|
|
Note that if you want to support adding/removing layers you should specify a list here.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `description`: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `layer`: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad.
|
|
- `suffix`: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `diff` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=diff_pcb/diff_sch, %x=pdf). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `add_link_id`: [boolean=false] When enabled we create a symlink to the output file with a name that contains the
|
|
git hashes involved in the comparison. If you plan to compress the output don't
|
|
forget to disable the `follow_links` option.
|
|
- `cache_dir`: [string=''] Directory to cache the intermediate files. Leave it blank to disable the cache.
|
|
- `copy_instead_of_link`: [boolean=false] Modifies the behavior of `add_link_id` to create a copy of the file instead of a
|
|
symlink. Useful for some Windows setups.
|
|
- `diff_mode`: [string='red_green'] [red_green,stats] In the `red_green` mode added stuff is green and red when removed.
|
|
The `stats` mode is used to meassure the amount of difference. In this mode all
|
|
changes are red, but you can abort if the difference is bigger than certain threshold.
|
|
- `force_checkout`: [boolean=false] When `old_type` and/or `new_type` are `git` KiBot will checkout the indicated point.
|
|
Before doing it KiBot will stash any change. Under some circumstances git could fail
|
|
to do a checkout, even after stashing, this option can workaround the problem.
|
|
Note that using it you could potentially lose modified files. For more information
|
|
read https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1248029/git-pull-error-entry-foo-not-uptodate-cannot-merge.
|
|
- `fuzz`: [number=5] [0,100] Color tolerance (fuzzyness) for the `stats` mode.
|
|
- `new`: [string|list(string)] The file you want to compare. Leave it blank for the current PCB/SCH.
|
|
A list is accepted only for the `multivar` type. Consult the `old` option for more information.
|
|
- `new_type`: [string='current'] [git,file,output,multivar,current] How to interpret the `new` name. Use `git` for a git hash, branch, etc.
|
|
Use `current` for the currently loaded PCB/Schematic.
|
|
Use `file` for a file name. Use `output` to specify the name of a `pcb_variant`/`sch_variant` output.
|
|
Use `multivar` to compare a set of variants, in this mode `new` is the list of variants.
|
|
If `old` is also `multivar` then it becomes the reference, otherwise we compare using pairs of variants.
|
|
- `old`: [string='HEAD'] Reference file. When using git use `HEAD` to refer to the last commit.
|
|
Use `HEAD~` to refer the previous to the last commit.
|
|
As `HEAD` is for the whole repo you can use `KIBOT_LAST-n` to make
|
|
reference to the changes in the PCB/SCH. The `n` value is how many
|
|
changes in the history you want to go back. A 0 is the same as `HEAD`,
|
|
a 1 means the last time the PCB/SCH was changed, etc.
|
|
Use `KIBOT_TAG-n` to search for the last tag skipping `n` tags.
|
|
Important: when using the `checkout` GitHub action you just get the
|
|
last commit. To clone the full repo use `fetch-depth: '0'`.
|
|
- `old_type`: [string='git'] [git,file,output,multivar] How to interpret the `old` name. Use `git` for a git hash, branch, etc.
|
|
Use `file` for a file name. Use `output` to specify the name of a `pcb_variant`/`sch_variant` output.
|
|
Use `multivar` to specify a reference file when `new_type` is also `multivar`.
|
|
- `only_different`: [boolean=false] Only include the pages with differences in the output PDF.
|
|
Note that when no differeces are found we get a page saying *No diff*.
|
|
- `pcb`: [boolean=true] Compare the PCB, otherwise compare the schematic.
|
|
- `threshold`: [number=0] [0,1000000] Error threshold for the `stats` mode, 0 is no error. When specified a
|
|
difference bigger than the indicated value will make the diff fail.
|
|
KiBot will return error level 29 and the diff generation will be aborted.
|
|
- `use_file_id`: [boolean=false] When creating the link name of an output file related to a variant use the variant
|
|
`file_id` instead of its name.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Datasheets downloader
|
|
* Type: `download_datasheets`
|
|
* Description: Downloads the datasheets for the project
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `download_datasheets` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`field`**: [string='Datasheet'] Name of the field containing the URL.
|
|
- `dnf`: [boolean=false] Include the DNF components.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `link_repeated`: [boolean=true] Instead of download things we already downloaded use symlinks.
|
|
- `output`: [string='${VALUE}.pdf'] Name used for the downloaded datasheet.
|
|
${FIELD} will be replaced by the FIELD content.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `repeated`: [boolean=false] Download URLs that we already downloaded.
|
|
It only makes sense if the `output` field makes their output different.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* DXF (Drawing Exchange Format)
|
|
* Type: `dxf`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB to 2D mechanical EDA tools (like AutoCAD).
|
|
This output is what you get from the File/Plot menu in pcbnew.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`layers`**: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user]
|
|
List of PCB layers to plot.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `description`: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `layer`: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad.
|
|
- `suffix`: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `dxf` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty.
|
|
IMPORTANT! KiCad will always create the file using its own name and then we can rename it.
|
|
For this reason you must avoid generating two variants at the same directory when one of
|
|
them uses the default KiCad name. Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`plot_sheet_reference`**: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result
|
|
(i.e. always the default worksheet style, also problems expanding text variables).
|
|
The `pcb_print` output can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs.
|
|
- `custom_reports`: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `content`: [string=''] Content for the report. Use ${basename} for the project name without extension.
|
|
Use ${filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER.
|
|
- `output`: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `drill_marks`: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale).
|
|
- `edge_cut_extension`: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot.
|
|
- `exclude_edge_layer`: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer.
|
|
- `exclude_pads_from_silkscreen`: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only).
|
|
- `force_plot_invisible_refs_vals`: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible.
|
|
- `inner_extension_pattern`: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers.
|
|
The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number.
|
|
Example '.g%n'.
|
|
- `metric_units`: [boolean=false] Use mm instead of inches.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_refs`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_values`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values.
|
|
- `polygon_mode`: [boolean=true] Plot using the contour, instead of the center line.
|
|
You must disable it to get the dimensions (See https://gitlab.com/kicad/code/kicad/-/issues/11901).
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `sketch_plot`: [boolean=false] Don't fill objects, just draw the outline.
|
|
- `tent_vias`: [boolean=true] Cover the vias.
|
|
- `uppercase_extensions`: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions.
|
|
- `use_aux_axis_as_origin`: [boolean=false] Use the auxiliary axis as origin for coordinates.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Excellon drill format
|
|
* Type: `excellon`
|
|
* Description: This is the main format for the drilling machine.
|
|
You can create a map file for documentation purposes.
|
|
This output is what you get from the 'File/Fabrication output/Drill Files' menu in pcbnew.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `excellon` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`metric_units`**: [boolean=true] Use metric units instead of inches.
|
|
- **`mirror_y_axis`**: [boolean=false] Invert the Y axis.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] name for the drill file, KiCad defaults if empty (%i='PTH_drill'). Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`pth_and_npth_single_file`**: [boolean=true] Generate one file for both, plated holes and non-plated holes, instead of two separated files.
|
|
- `left_digits`: [number=0] number of digits for integer part of coordinates (0 is auto).
|
|
- `map`: [dict|string] [hpgl,ps,gerber,dxf,svg,pdf] Format for a graphical drill map.
|
|
Not generated unless a format is specified.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the map file, KiCad defaults if empty (%i='PTH_drill_map'). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `type`: [string='pdf'] [hpgl,ps,gerber,dxf,svg,pdf] Format for a graphical drill map.
|
|
- `minimal_header`: [boolean=false] Use a minimal header in the file.
|
|
- `npth_id`: [string] Force this replacement for %i when generating NPTH files.
|
|
- `pth_id`: [string] Force this replacement for %i when generating PTH and unified files.
|
|
- `report`: [dict|string] Name of the drill report. Not generated unless a name is specified.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `filename`: [string=''] Name of the drill report. Not generated unless a name is specified.
|
|
(%i='drill_report' %x='txt').
|
|
- `right_digits`: [number=0] number of digits for mantissa part of coordinates (0 is auto).
|
|
- `route_mode_for_oval_holes`: [boolean=true] Use route command for oval holes (G00), otherwise use G85.
|
|
- `use_aux_axis_as_origin`: [boolean=false] Use the auxiliary axis as origin for coordinates.
|
|
- `zeros_format`: [string='DECIMAL_FORMAT'] [DECIMAL_FORMAT,SUPPRESS_LEADING,SUPPRESS_TRAILING,KEEP_ZEROS] How to handle the zeros.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* GenCAD
|
|
* Type: `gencad`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB in GENCAD format.
|
|
This format is interpreted by some CADCAM software and helps certain
|
|
manufacturers
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `gencad` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=gencad, %x=cad). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `aux_origin`: [boolean=false] Use auxiliary axis as origin.
|
|
- `flip_bottom_padstacks`: [boolean=false] Flip bottom footprint padstacks.
|
|
- `no_reuse_shapes`: [boolean=false] Generate a new shape for each footprint instance (Do not reuse shapes).
|
|
- `save_origin`: [boolean=false] Save the origin coordinates in the file.
|
|
- `unique_pin_names`: [boolean=false] Generate unique pin names.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Gerber drill format
|
|
* Type: `gerb_drill`
|
|
* Description: This is the information for the drilling machine in gerber format.
|
|
You can create a map file for documentation purposes.
|
|
This output is what you get from the 'File/Fabrication output/Drill Files' menu in pcbnew.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `gerb_drill` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] name for the drill file, KiCad defaults if empty (%i='PTH_drill'). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `map`: [dict|string] [hpgl,ps,gerber,dxf,svg,pdf] Format for a graphical drill map.
|
|
Not generated unless a format is specified.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the map file, KiCad defaults if empty (%i='PTH_drill_map'). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `type`: [string='pdf'] [hpgl,ps,gerber,dxf,svg,pdf] Format for a graphical drill map.
|
|
- `npth_id`: [string] Force this replacement for %i when generating NPTH files.
|
|
- `pth_id`: [string] Force this replacement for %i when generating PTH and unified files.
|
|
- `report`: [dict|string] Name of the drill report. Not generated unless a name is specified.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `filename`: [string=''] Name of the drill report. Not generated unless a name is specified.
|
|
(%i='drill_report' %x='txt').
|
|
- `use_aux_axis_as_origin`: [boolean=false] Use the auxiliary axis as origin for coordinates.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Gerber format
|
|
* Type: `gerber`
|
|
* Description: This is the main fabrication format for the PCB.
|
|
This output is what you get from the File/Plot menu in pcbnew.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`layers`**: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user]
|
|
List of PCB layers to plot.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `description`: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `layer`: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad.
|
|
- `suffix`: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `gerber` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`create_gerber_job_file`**: [boolean=true] Creates a file with information about all the generated gerbers.
|
|
You can use it in gerbview to load all gerbers at once.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty.
|
|
IMPORTANT! KiCad will always create the file using its own name and then we can rename it.
|
|
For this reason you must avoid generating two variants at the same directory when one of
|
|
them uses the default KiCad name. Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`plot_sheet_reference`**: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result
|
|
(i.e. always the default worksheet style, also problems expanding text variables).
|
|
The `pcb_print` output can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs.
|
|
- **`subtract_mask_from_silk`**: [boolean=false] Subtract the solder mask from the silk screen.
|
|
- **`use_gerber_net_attributes`**: [boolean=true] Include netlist metadata.
|
|
- **`use_gerber_x2_attributes`**: [boolean=true] Use the extended X2 format (otherwise use X1 formerly RS-274X).
|
|
- **`use_protel_extensions`**: [boolean=false] Use legacy Protel file extensions.
|
|
- `custom_reports`: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `content`: [string=''] Content for the report. Use ${basename} for the project name without extension.
|
|
Use ${filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER.
|
|
- `output`: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
|
|
- `disable_aperture_macros`: [boolean=false] Disable aperture macros (workaround for buggy CAM software) (KiCad 6).
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `edge_cut_extension`: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot.
|
|
- `exclude_edge_layer`: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer.
|
|
- `exclude_pads_from_silkscreen`: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only).
|
|
- `force_plot_invisible_refs_vals`: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible.
|
|
- `gerber_job_file`: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the gerber job file (%i='job', %x='gbrjob'). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `gerber_precision`: [number=4.6] This the gerber coordinate format, can be 4.5 or 4.6.
|
|
- `inner_extension_pattern`: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers.
|
|
The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number.
|
|
Example '.g%n'.
|
|
- `line_width`: [number=0.1] [0.02,2] Line_width for objects without width [mm] (KiCad 5).
|
|
- `plot_footprint_refs`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_values`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `tent_vias`: [boolean=true] Cover the vias.
|
|
- `uppercase_extensions`: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions.
|
|
- `use_aux_axis_as_origin`: [boolean=false] Use the auxiliary axis as origin for coordinates.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* HPGL (Hewlett & Packard Graphics Language)
|
|
* Type: `hpgl`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB for plotters and laser printers.
|
|
This output is what you get from the File/Plot menu in pcbnew.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`layers`**: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user]
|
|
List of PCB layers to plot.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `description`: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `layer`: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad.
|
|
- `suffix`: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `hpgl` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty.
|
|
IMPORTANT! KiCad will always create the file using its own name and then we can rename it.
|
|
For this reason you must avoid generating two variants at the same directory when one of
|
|
them uses the default KiCad name. Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`plot_sheet_reference`**: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result
|
|
(i.e. always the default worksheet style, also problems expanding text variables).
|
|
The `pcb_print` output can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs.
|
|
- `custom_reports`: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `content`: [string=''] Content for the report. Use ${basename} for the project name without extension.
|
|
Use ${filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER.
|
|
- `output`: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `drill_marks`: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale).
|
|
- `edge_cut_extension`: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot.
|
|
- `exclude_edge_layer`: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer.
|
|
- `exclude_pads_from_silkscreen`: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only).
|
|
- `force_plot_invisible_refs_vals`: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible.
|
|
- `inner_extension_pattern`: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers.
|
|
The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number.
|
|
Example '.g%n'.
|
|
- `mirror_plot`: [boolean=false] Plot mirrored.
|
|
- `pen_number`: [number=1] [1,16] Pen number.
|
|
- `pen_speed`: [number=20] [1,99] Pen speed.
|
|
- `pen_width`: [number=15] [0,100] Pen diameter in MILS, useful to fill areas. However, it is in mm in HPGL files.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_refs`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_values`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `scaling`: [number=0] Scale factor (0 means autoscaling).
|
|
- `sketch_plot`: [boolean=false] Don't fill objects, just draw the outline.
|
|
- `tent_vias`: [boolean=true] Cover the vias.
|
|
- `uppercase_extensions`: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* IBoM (Interactive HTML BoM)
|
|
* Type: `ibom`
|
|
* Description: Generates an interactive web page useful to identify the position of the components in the PCB.
|
|
For more information: https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/InteractiveHtmlBom
|
|
This output is what you get from the InteractiveHtmlBom plug-in (pcbnew).
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `ibom` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`board_rotation`**: [number=0] Board rotation in degrees (-180 to 180). Will be rounded to multiple of 5.
|
|
- **`bom_view`**: [string='left-right'] [bom-only,left-right,top-bottom] Default BOM view.
|
|
- **`extra_fields`**: [string=''] Comma separated list of extra fields to pull from netlist or xml file.
|
|
Using 'X,Y' is a shortcut for `show_fields` and `group_fields` with values 'Value,Footprint,X,Y'.
|
|
- **`include_tracks`**: [boolean=false] Include track/zone information in output. F.Cu and B.Cu layers only.
|
|
- **`layer_view`**: [string='FB'] [F,FB,B] Default layer view.
|
|
- **`normalize_field_case`**: [boolean=false] Normalize extra field name case. E.g. 'MPN' and 'mpn' will be considered the same field.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output, use '' to use the IBoM filename (%i=ibom, %x=html). Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`show_fields`**: [string=''] Comma separated list of fields to show in the BOM.
|
|
Value and Footprint are displayed when nothing is specified.
|
|
- `blacklist`: [string=''] List of comma separated blacklisted components or prefixes with *. E.g. 'X1,MH*'.
|
|
IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters.
|
|
- `blacklist_empty_val`: [boolean=false] Blacklist components with empty value.
|
|
IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters.
|
|
- `checkboxes`: [string='Sourced,Placed'] Comma separated list of checkbox columns.
|
|
- `dark_mode`: [boolean=false] Default to dark mode.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
Avoid using it in conjunction with IBoM native filtering options.
|
|
- `dnp_field`: [string=''] Name of the extra field that indicates do not populate status.
|
|
Components with this field not empty will be blacklisted.
|
|
IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters.
|
|
- `extra_data_file`: [string=''] Path to netlist or xml file. You can use '%F.xml' to avoid specifying the project name.
|
|
Leave it blank for most uses, data will be extracted from the PCB.
|
|
- `group_fields`: [string=''] Comma separated list of fields that components will be grouped by.
|
|
Value and Footprint are used when nothing is specified.
|
|
- `hide_pads`: [boolean=false] Hide footprint pads by default.
|
|
- `hide_silkscreen`: [boolean=false] Hide silkscreen by default.
|
|
- `highlight_pin1`: [boolean=false] Highlight pin1 by default.
|
|
- `include_nets`: [boolean=false] Include netlist information in output..
|
|
- `name_format`: [string='ibom'] Output file name format supports substitutions:
|
|
%f : original pcb file name without extension.
|
|
%p : pcb/project title from pcb metadata.
|
|
%c : company from pcb metadata.
|
|
%r : revision from pcb metadata.
|
|
%d : pcb date from metadata if available, file modification date otherwise.
|
|
%D : bom generation date.
|
|
%T : bom generation time.
|
|
Extension .html will be added automatically.
|
|
Note that this name is used only when output is ''.
|
|
- *netlist_file*: Alias for extra_data_file.
|
|
- `no_blacklist_virtual`: [boolean=false] Do not blacklist virtual components.
|
|
IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters.
|
|
- `no_compression`: [boolean=false] Disable compression of pcb data.
|
|
- `no_redraw_on_drag`: [boolean=false] Do not redraw pcb on drag by default.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `show_fabrication`: [boolean=false] Show fabrication layer by default.
|
|
- `sort_order`: [string='C,R,L,D,U,Y,X,F,SW,A,~,HS,CNN,J,P,NT,MH'] Default sort order for components. Must contain '~' once.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
Avoid using it in conjunction with IBoM native filtering options.
|
|
- `variant_field`: [string=''] Name of the extra field that stores board variant for component.
|
|
IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters.
|
|
- `variants_blacklist`: [string=''] List of board variants to exclude from the BOM.
|
|
IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters.
|
|
- `variants_whitelist`: [string=''] List of board variants to include in the BOM.
|
|
IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Info
|
|
* Type: `info`
|
|
* Description: Records information about the current run.
|
|
It can be used to know more about the environment used to generate the files.
|
|
Please don't rely on the way things are reported, its content could change,
|
|
adding or removing information
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `info` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=info, %x=txt). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `environment`: [string='names'] [names,none,full] List environment variables.
|
|
IMPORTANT: Don't use `full` unless you know you are not leaking sensitive information.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* KiBoM (KiCad Bill of Materials)
|
|
* Type: `kibom`
|
|
* Description: Used to generate the BoM in HTML or CSV format using the KiBoM plug-in.
|
|
For more information: https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBoM
|
|
Note that this output is provided as a compatibility tool.
|
|
We recommend using the `bom` output instead.
|
|
This output is what you get from the 'Tools/Generate Bill of Materials' menu in eeschema.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `kibom` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`format`**: [string='HTML'] [HTML,CSV,XML,XLSX] Format for the BoM.
|
|
- **`number`**: [number=1] Number of boards to build (components multiplier).
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=bom). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `conf`: [string|dict] BoM configuration file, relative to PCB. Environment variables and ~ allowed.
|
|
You can also define the configuration here, will be stored in `config.kibom.ini`.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`columns`**: [list(dict)|list(string)] List of columns to display.
|
|
Can be just the name of the field.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`field`**: [string=''] Name of the field to use for this column.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Name to display in the header. The field is used when empty.
|
|
- `join`: [list(string)|string=''] List of fields to join to this column.
|
|
- **`fit_field`**: [string='Config'] Field name used to determine if a particular part is to be fitted (also DNC and variants).
|
|
- **`group_fields`**: [list(string)] List of fields used for sorting individual components into groups.
|
|
Components which match (comparing *all* fields) will be grouped together.
|
|
Field names are case-insensitive.
|
|
If empty: ['Part', 'Part Lib', 'Value', 'Footprint', 'Footprint Lib'] is used.
|
|
- **`ignore_dnf`**: [boolean=true] Exclude DNF (Do Not Fit) components.
|
|
- **`number_rows`**: [boolean=true] First column is the row number.
|
|
- `component_aliases`: [list(list(string))] A series of values which are considered to be equivalent for the part name.
|
|
Each entry is a list of equivalen names. Example: ['c', 'c_small', 'cap' ]
|
|
will ensure the equivalent capacitor symbols can be grouped together.
|
|
If empty the following aliases are used:
|
|
- ['r', 'r_small', 'res', 'resistor']
|
|
- ['l', 'l_small', 'inductor']
|
|
- ['c', 'c_small', 'cap', 'capacitor']
|
|
- ['sw', 'switch']
|
|
- ['zener', 'zenersmall']
|
|
- ['d', 'diode', 'd_small'].
|
|
- `datasheet_as_link`: [string=''] Column with links to the datasheet (HTML only).
|
|
- `digikey_link`: [string|list(string)=''] Column/s containing Digi-Key part numbers, will be linked to web page (HTML only).
|
|
- `exclude_any`: [list(dict)] A series of regular expressions used to exclude parts.
|
|
If a component matches ANY of these, it will be excluded.
|
|
Column names are case-insensitive.
|
|
If empty the following list is used:
|
|
- column: References
|
|
regex: '^TP[0-9]*'
|
|
- column: References
|
|
regex: '^FID'
|
|
- column: Part
|
|
regex: 'mount.*hole'
|
|
- column: Part
|
|
regex: 'solder.*bridge'
|
|
- column: Part
|
|
regex: 'test.*point'
|
|
- column: Footprint
|
|
regex 'test.*point'
|
|
- column: Footprint
|
|
regex: 'mount.*hole'
|
|
- column: Footprint
|
|
regex: 'fiducial'.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `column`: [string=''] Name of the column to apply the regular expression.
|
|
- *field*: Alias for column.
|
|
- `regex`: [string=''] Regular expression to match.
|
|
- *regexp*: Alias for regex.
|
|
- `group_connectors`: [boolean=true] Connectors with the same footprints will be grouped together, independent of the name of the connector.
|
|
- `hide_headers`: [boolean=false] Hide column headers.
|
|
- `hide_pcb_info`: [boolean=false] Hide project information.
|
|
- `html_generate_dnf`: [boolean=true] Generate a separated section for DNF (Do Not Fit) components (HTML only).
|
|
- `include_only`: [list(dict)] A series of regular expressions used to select included parts.
|
|
If there are any regex defined here, only components that match against ANY of them will be included.
|
|
Column names are case-insensitive.
|
|
If empty all the components are included.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `column`: [string=''] Name of the column to apply the regular expression.
|
|
- *field*: Alias for column.
|
|
- `regex`: [string=''] Regular expression to match.
|
|
- *regexp*: Alias for regex.
|
|
- `merge_blank_fields`: [boolean=true] Component groups with blank fields will be merged into the most compatible group, where possible.
|
|
- `ref_separator`: [string=' '] Separator used for the list of references.
|
|
- `test_regex`: [boolean=true] Each component group will be tested against a number of regular-expressions (see ``)..
|
|
- `use_alt`: [boolean=false] Print grouped references in the alternate compressed style eg: R1-R7,R18.
|
|
- `separator`: [string=','] CSV Separator.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant(s), used to determine which components
|
|
are output to the BoM. To specify multiple variants,
|
|
with a BOM file exported for each variant, separate
|
|
variants with the ';' (semicolon) character.
|
|
This isn't related to the KiBot concept of variants.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* KiCost (KiCad Cost calculator)
|
|
* Type: `kicost`
|
|
* Description: Generates a spreadsheet containing components costs.
|
|
For more information: https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiCost
|
|
This output is what you get from the KiCost plug-in (eeschema).
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `kicost` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- *board_qty*: Alias for number.
|
|
- **`currency`**: [string|list(string)=USD] Currency priority. Use ISO4217 codes (i.e. USD, EUR).
|
|
- **`distributors`**: [string|list(string)] Include this distributors list. Default is all the available.
|
|
- **`no_distributors`**: [string|list(string)] Exclude this distributors list. They are removed after computing `distributors`.
|
|
- **`no_price`**: [boolean=false] Do not look for components price. For testing purposes.
|
|
- **`number`**: [number=100] Number of boards to build (components multiplier).
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=kicost, %x=xlsx). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `aggregate`: [list(dict)] Add components from other projects.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- *board_qty*: Alias for number.
|
|
- **`file`**: [string=''] Name of the XML to aggregate.
|
|
- **`number`**: [number=100] Number of boards to build (components multiplier).
|
|
- `variant`: [string=' '] Variant for this project.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
Don't use the `kicost_variant` when using internal variants/filters.
|
|
- `fields`: [string|list(string)] List of fields to be added to the global data section.
|
|
- `group_fields`: [string|list(string)] List of fields that can be different for a group.
|
|
Parts with differences in these fields are grouped together, but displayed individually.
|
|
- `ignore_fields`: [string|list(string)] List of fields to be ignored.
|
|
- `kicost_variant`: [string=''] Regular expression to match the variant field (KiCost option, not internal variants).
|
|
- `no_collapse`: [boolean=false] Do not collapse the part references (collapse=R1-R4).
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `show_cat_url`: [boolean=false] Include the catalogue links in the catalogue code.
|
|
- `split_extra_fields`: [string|list(string)] Declare part fields to include in multipart split process.
|
|
- `translate_fields`: [list(dict)] Fields to rename (KiCost option, not internal filters).
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `field`: [string=''] Name of the field to rename.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] New name.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
Don't use the `kicost_variant` when using internal variants/filters.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Navigate Results
|
|
* Type: `navigate_results`
|
|
* Description: Generates a web page to navigate the generated outputs
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `navigate_results` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`link_from_root`**: [string=''] The name of a file to create at the main output directory linking to the home page.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=html, %x=navigate). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=10] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Netlist
|
|
* Type: `netlist`
|
|
* Description: Generates the list of connections for the project.
|
|
The netlist can be generated in the classic format and in IPC-D-356 format,
|
|
useful for board testing
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `netlist` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`format`**: [string='classic'] [classic,ipc] The `classic` format is the KiCad internal format, and is generated
|
|
from the schematic. The `ipc` format is the IPC-D-356 format, useful for PCB
|
|
testing, is generated from the PCB.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=netlist/IPC-D-356, %x=net/d356). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* PCB Print
|
|
* Type: `pcb_print`
|
|
* Description: Prints the PCB using a mechanism that is more flexible than `pdf_pcb_print` and `svg_pcb_print`.
|
|
Supports PDF, SVG, PNG, EPS and PS formats.
|
|
KiCad 5: including the frame is slow.
|
|
KiCad 6: for custom frames use the `enable_ki6_frame_fix`, is slow.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `pcb_print` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`color_theme`**: [string='_builtin_classic'] Selects the color theme. Only applies to KiCad 6.
|
|
To use the KiCad 6 default colors select `_builtin_default`.
|
|
Usually user colors are stored as `user`, but you can give it another name.
|
|
- **`force_edge_cuts`**: [boolean=false] Add the `Edge.Cuts` to all the pages.
|
|
- **`format`**: [string='PDF'] [PDF,SVG,PNG,EPS,PS] Format for the output file/s.
|
|
Note that for PS you need `ghostscript` which isn't part of the default docker images.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=assembly, %x=pdf/ps)/(%i=assembly_page_NN, %x=svg/png/eps).
|
|
Consult the `page_number_as_extension` and `page_id` options. Affected by global options.
|
|
- *output_name*: Alias for output.
|
|
- **`pages`**: [list(dict)] List of pages to include in the output document.
|
|
Each page contains one or more layers of the PCB.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`layers`**: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] List of layers printed in this page.
|
|
Order is important, the last goes on top.
|
|
You can reuse other layers lists, some options aren't used here, but they are valid.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `color`: [string=''] Color used for this layer.
|
|
- `description`: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `force_plot_invisible_refs_vals`: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible.
|
|
- `layer`: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_refs`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_values`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values.
|
|
- `suffix`: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
|
|
- **`scaling`**: [number=1.0] Scale factor (0 means autoscaling).
|
|
- **`sort_layers`**: [boolean=false] Try to sort the layers in the same order that uses KiCad for printing.
|
|
- `colored_holes`: [boolean=true] Change the drill holes to be colored instead of white.
|
|
- `exclude_pads_from_silkscreen`: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only).
|
|
- `holes_color`: [string='#000000'] Color used for the holes when `colored_holes` is enabled.
|
|
- `line_width`: [number=0.1] [0.02,2] For objects without width [mm] (KiCad 5).
|
|
- `mirror`: [boolean=false] Print mirrored (X axis inverted).
|
|
- `monochrome`: [boolean=false] Print in gray scale.
|
|
- `negative_plot`: [boolean=false] Invert black and white. Only useful for a single layer.
|
|
- `page_id`: [string='%02d'] Text to differentiate the pages. Use %d (like in C) to get the page number.
|
|
- `sheet`: [string='Assembly'] Text to use for the `sheet` in the title block.
|
|
- `sheet_reference_color`: [string=''] Color to use for the frame and title block.
|
|
- `tent_vias`: [boolean=true] Cover the vias.
|
|
- `title`: [string=''] Text used to replace the sheet title. %VALUE expansions are allowed.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the text is concatenated.
|
|
- **`plot_sheet_reference`**: [boolean=true] Include the title-block (worksheet, frame, etc.).
|
|
- **`scaling`**: [number=1.0] Default scale factor (0 means autoscaling).
|
|
- `add_background`: [boolean=false] Add a background to the pages, see `background_color`.
|
|
- `background_color`: [string='#FFFFFF'] Color for the background when `add_background` is enabled.
|
|
- `background_image`: [string=''] Background image, must be an SVG, only when `add_background` is enabled.
|
|
- `blind_via_color`: [string=''] Color used for blind/buried `colored_vias`.
|
|
- `colored_pads`: [boolean=true] Plot through-hole in a different color. Like KiCad GUI does.
|
|
- `colored_vias`: [boolean=true] Plot vias in a different color. Like KiCad GUI does.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `dpi`: [number=360] [36,1200] Resolution (Dots Per Inch) for the output file. Most objects are vectors, but thing
|
|
like the the solder mask are handled as images by the conversion tools.
|
|
- `drill_marks`: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale).
|
|
- `forced_edge_cuts_color`: [string=''] Color used for the `force_edge_cuts` option.
|
|
- `frame_plot_mechanism`: [string='internal'] [gui,internal,plot] Plotting the frame from Python is problematic.
|
|
This option selects a workaround strategy.
|
|
gui: uses KiCad GUI to do it. Is slow but you get the correct frame.
|
|
But it can't keep track of page numbers.
|
|
internal: KiBot loads the `.kicad_wks` and does the drawing work.
|
|
Best option, but some details are different from what the GUI generates.
|
|
plot: uses KiCad Python API. Only available for KiCad 6.
|
|
You get the default frame and some substitutions doesn't work.
|
|
- `hide_excluded`: [boolean=false] Hide components in the Fab layer that are marked as excluded by a variant.
|
|
Affected by global options.
|
|
- `keep_temporal_files`: [boolean=false] Store the temporal page and layer files in the output dir and don't delete them.
|
|
- `micro_via_color`: [string=''] Color used for micro `colored_vias`.
|
|
- `pad_color`: [string=''] Color used for `colored_pads`.
|
|
- `page_number_as_extension`: [boolean=false] When enabled the %i is always `assembly`, the %x will be NN.FORMAT (i.e. 01.png).
|
|
Note: page numbers can be customized using the `page_id` option for each page.
|
|
- `png_width`: [number=1280] [0,7680] Width of the PNG in pixels. Use 0 to use as many pixels as the DPI needs for the page size.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `realistic_solder_mask`: [boolean=true] Try to draw the solder mask as a real solder mask, not the negative used for fabrication.
|
|
In order to get a good looking select a color with transparency, i.e. '#14332440'.
|
|
PcbDraw must be installed in order to use this option.
|
|
- `sheet_reference_layout`: [string=''] Worksheet file (.kicad_wks) to use. Leave empty to use the one specified in the project.
|
|
- `title`: [string=''] Text used to replace the sheet title. %VALUE expansions are allowed.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the text is concatenated.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `via_color`: [string=''] Color used for through-hole `colored_vias`.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* PCB with variant generator
|
|
* Type: `pcb_variant`
|
|
* Description: Creates a copy of the PCB with all the filters and variants applied.
|
|
This copy isn't intended for development.
|
|
Is just a tweaked version of the original where you can look at the results.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `pcb_variant` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=variant, %x=kicad_pcb). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `copy_project`: [boolean=true] Copy the KiCad project to the destination directory.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `hide_excluded`: [boolean=false] Hide components in the Fab layer that are marked as excluded by a variant.
|
|
Affected by global options.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `title`: [string=''] Text used to replace the sheet title. %VALUE expansions are allowed.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the text is concatenated.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* PcbDraw - Beautiful 2D PCB render
|
|
* Type: `pcbdraw`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB as a 2D model (SVG, PNG or JPG).
|
|
Uses configurable colors.
|
|
Can also render the components if the 2D models are available
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `pcbdraw` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`bottom`**: [boolean=false] Render the bottom side of the board (default is top side).
|
|
- **`format`**: [string='svg'] [svg,png,jpg] Output format. Only used if no `output` is specified.
|
|
- **`mirror`**: [boolean=false] Mirror the board.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the generated file. Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`show_components`**: [list(string)|string=none] [none,all] List of components to draw, can be also a string for none or all.
|
|
The default is none.
|
|
- **`style`**: [string|dict] PCB style (colors). An internal name, the name of a JSON file or the style options.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`board`**: [string='#208b47'] Color for the board without copper (covered by solder mask).
|
|
- **`clad`**: [string='#cabb3e'] Color for the PCB core (not covered by solder mask).
|
|
- **`copper`**: [string='#285e3a'] Color for the copper zones (covered by solder mask).
|
|
- **`outline`**: [string='#000000'] Color for the outline.
|
|
- **`pads`**: [string='#8b898c'] Color for the exposed pads (metal finish).
|
|
- **`silk`**: [string='#d5dce4'] Color for the silk screen.
|
|
- `highlight_on_top`: [boolean=false] Highlight over the component (not under).
|
|
- `highlight_padding`: [number=1.5] [0,1000] how much the highlight extends around the component [mm].
|
|
- `highlight_style`: [string='stroke:none;fill:#ff0000;opacity:0.5;'] SVG code for the highlight style.
|
|
- `vcut`: [string='#bf2600'] Color for the V-CUTS.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `dpi`: [number=300] [10,1200] Dots per inch (resolution) of the generated image.
|
|
- `highlight`: [list(string)=[]] List of components to highlight.
|
|
- `libs`: [list(string)=[]] List of libraries.
|
|
- `no_drillholes`: [boolean=false] Do not make holes transparent.
|
|
- `placeholder`: [boolean=false] Show placeholder for missing components.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `remap`: [dict|None] Replacements for PCB references using components (lib:component).
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `vcuts`: [boolean=false] Render V-CUTS on the Cmts.User layer.
|
|
- `warnings`: [string='visible'] [visible,all,none] Using visible only the warnings about components in the visible side are generated.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* PDF (Portable Document Format)
|
|
* Type: `pdf`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB to the most common exchange format. Suitable for printing.
|
|
Note that this output isn't the best for documating your project.
|
|
This output is what you get from the File/Plot menu in pcbnew.
|
|
The `pcb_print` is usually a better alternative.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`layers`**: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user]
|
|
List of PCB layers to plot.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `description`: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `layer`: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad.
|
|
- `suffix`: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `pdf` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty.
|
|
IMPORTANT! KiCad will always create the file using its own name and then we can rename it.
|
|
For this reason you must avoid generating two variants at the same directory when one of
|
|
them uses the default KiCad name. Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`plot_sheet_reference`**: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result
|
|
(i.e. always the default worksheet style, also problems expanding text variables).
|
|
The `pcb_print` output can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs.
|
|
- `custom_reports`: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `content`: [string=''] Content for the report. Use ${basename} for the project name without extension.
|
|
Use ${filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER.
|
|
- `output`: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `drill_marks`: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale).
|
|
- `edge_cut_extension`: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot.
|
|
- `exclude_edge_layer`: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer.
|
|
- `exclude_pads_from_silkscreen`: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only).
|
|
- `force_plot_invisible_refs_vals`: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible.
|
|
- `inner_extension_pattern`: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers.
|
|
The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number.
|
|
Example '.g%n'.
|
|
- `line_width`: [number=0.1] [0.02,2] For objects without width [mm] (KiCad 5).
|
|
- `mirror_plot`: [boolean=false] Plot mirrored.
|
|
- `negative_plot`: [boolean=false] Invert black and white.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_refs`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_values`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `tent_vias`: [boolean=true] Cover the vias.
|
|
- `uppercase_extensions`: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty.
|
|
IMPORTANT! KiCad will always create the file using its own name and then we can rename it.
|
|
For this reason you must avoid generating two variants at the same directory when one of
|
|
them uses the default KiCad name. Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`plot_sheet_reference`**: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result
|
|
(i.e. always the default worksheet style, also problems expanding text variables).
|
|
The `pcb_print` output can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `custom_reports`: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `content`: [string=''] Content for the report. Use ${basename} for the project name without extension.
|
|
Use ${filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER.
|
|
- `output`: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `drill_marks`: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale).
|
|
- `edge_cut_extension`: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot.
|
|
- `exclude_edge_layer`: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer.
|
|
- `exclude_pads_from_silkscreen`: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only).
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `force_plot_invisible_refs_vals`: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible.
|
|
- `inner_extension_pattern`: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers.
|
|
The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number.
|
|
Example '.g%n'.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_refs`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_values`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
- `tent_vias`: [boolean=true] Cover the vias.
|
|
- `uppercase_extensions`: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
|
|
* PDF PCB Print (Portable Document Format)
|
|
* Type: `pdf_pcb_print`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB to the most common exchange format. Suitable for printing.
|
|
This is the main format to document your PCB.
|
|
This output is what you get from the 'File/Print' menu in pcbnew.
|
|
The `pcb_print` is usually a better alternative.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`layers`**: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user]
|
|
List of PCB layers to include in the PDF.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `description`: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `layer`: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad.
|
|
- `suffix`: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `pdf_pcb_print` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`plot_sheet_reference`**: [boolean=true] Include the title-block.
|
|
- **`scaling`**: [number=1.0] Scale factor (0 means autoscaling). You should disable `plot_sheet_reference` when using it.
|
|
- **`separated`**: [boolean=false] Print layers in separated pages.
|
|
- `color_theme`: [string='_builtin_classic'] Selects the color theme. Onlyu applies to KiCad 6.
|
|
To use the KiCad 6 default colors select `_builtin_default`.
|
|
Usually user colors are stored as `user`, but you can give it another name.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `drill_marks`: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale).
|
|
- `force_edge_cuts`: [boolean=true] Only useful for KiCad 6 when printing in one page, you can disable the edge here.
|
|
KiCad 5 forces it by default, and you can't control it from config files.
|
|
Same for KiCad 6 when printing to separated pages.
|
|
- `hide_excluded`: [boolean=false] Hide components in the Fab layer that are marked as excluded by a variant.
|
|
Affected by global options.
|
|
- `mirror`: [boolean=false] Print mirrored (X axis inverted). ONLY for KiCad 6.
|
|
- `monochrome`: [boolean=false] Print in black and white.
|
|
- `output`: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output PDF (%i=layers, %x=pdf). Affected by global options.
|
|
- *output_name*: Alias for output.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `title`: [string=''] Text used to replace the sheet title. %VALUE expansions are allowed.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the text is concatenated.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* PDF Schematic Print (Portable Document Format)
|
|
* Type: `pdf_sch_print`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB to the most common exchange format. Suitable for printing.
|
|
This is the main format to document your schematic.
|
|
This output is what you get from the 'File/Print' menu in eeschema.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `pdf_sch_print` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`frame`**: [boolean=true] Include the frame and title block.
|
|
- `all_pages`: [boolean=true] Generate with all hierarchical sheets.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `monochrome`: [boolean=false] Generate a monochromatic PDF.
|
|
- `output`: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output PDF (%i=schematic, %x=pdf). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
Not fitted components are crossed.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* PDF joiner
|
|
* Type: `pdfunite`
|
|
* Description: Generates a new PDF from other outputs.
|
|
This is just a PDF joiner, using `pdfunite` from Poppler Utils.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `pdfunite` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the generated PDF (%i=name of the output %x=pdf). Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`outputs`**: [list(dict)] Which files will be included.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`from_output`**: [string=''] Collect files from the selected output.
|
|
When used the `source` option is ignored.
|
|
- **`source`**: [string='*.pdf'] File names to add, wildcards allowed. Use ** for recursive match.
|
|
By default this pattern is applied to the output dir specified with `-d` command line option.
|
|
See the `from_cwd` option.
|
|
- `filter`: [string='.*\.pdf'] A regular expression that source files must match.
|
|
- `from_cwd`: [boolean=false] Use the current working directory instead of the dir specified by `-d`.
|
|
- `use_external_command`: [boolean=false] Use the `pdfunite` tool instead of PyPDF2 Python module.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Pick & place
|
|
* Type: `position`
|
|
* Description: Generates the file with position information for the PCB components, used by the pick and place machine.
|
|
This output is what you get from the 'File/Fabrication output/Footprint position (.pos) file' menu in pcbnew.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `position` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`format`**: [string='ASCII'] [ASCII,CSV] Format for the position file.
|
|
- **`only_smd`**: [boolean=true] Only include the surface mount components.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name (%i='top_pos'|'bottom_pos'|'both_pos', %x='pos'|'csv').
|
|
Important: when using separate files you must use `%i` to differentiate them. Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`separate_files_for_front_and_back`**: [boolean=true] Generate two separated files, one for the top and another for the bottom.
|
|
- **`units`**: [string='millimeters'] [millimeters,inches,mils] Units used for the positions. Affected by global options.
|
|
- `bottom_negative_x`: [boolean=false] Use negative X coordinates for footprints on bottom layer.
|
|
- `columns`: [list(dict)|list(string)] Which columns are included in the output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`id`**: [string=''] [Ref,Val,Package,PosX,PosY,Rot,Side] Internal name.
|
|
- `name`: [string=''] Name to use in the output file. The id is used when empty.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `include_virtual`: [boolean=false] Include virtual components. For special purposes, not pick & place.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `right_digits`: [number=4] number of digits for mantissa part of coordinates (0 is auto).
|
|
- `use_aux_axis_as_origin`: [boolean=true] Use the auxiliary axis as origin for coordinates (KiCad default).
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* PS (Postscript)
|
|
* Type: `ps`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB to a format suitable for printing.
|
|
This output is what you get from the File/Plot menu in pcbnew.
|
|
The `pcb_print` is usually a better alternative.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`layers`**: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user]
|
|
List of PCB layers to plot.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `description`: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `layer`: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad.
|
|
- `suffix`: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `ps` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty.
|
|
IMPORTANT! KiCad will always create the file using its own name and then we can rename it.
|
|
For this reason you must avoid generating two variants at the same directory when one of
|
|
them uses the default KiCad name. Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`plot_sheet_reference`**: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result
|
|
(i.e. always the default worksheet style, also problems expanding text variables).
|
|
The `pcb_print` output can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs.
|
|
- **`scaling`**: [number=1] Scale factor (0 means autoscaling).
|
|
- `a4_output`: [boolean=true] Force A4 paper size.
|
|
- `custom_reports`: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `content`: [string=''] Content for the report. Use ${basename} for the project name without extension.
|
|
Use ${filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER.
|
|
- `output`: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `drill_marks`: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale).
|
|
- `edge_cut_extension`: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot.
|
|
- `exclude_edge_layer`: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer.
|
|
- `exclude_pads_from_silkscreen`: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only).
|
|
- `force_plot_invisible_refs_vals`: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible.
|
|
- `inner_extension_pattern`: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers.
|
|
The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number.
|
|
Example '.g%n'.
|
|
- `line_width`: [number=0.15] [0.02,2] For objects without width [mm] (KiCad 5).
|
|
- `mirror_plot`: [boolean=false] Plot mirrored.
|
|
- `negative_plot`: [boolean=false] Invert black and white.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_refs`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_values`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `scale_adjust_x`: [number=1.0] Fine grain adjust for the X scale (floating point multiplier).
|
|
- `scale_adjust_y`: [number=1.0] Fine grain adjust for the Y scale (floating point multiplier).
|
|
- `sketch_plot`: [boolean=false] Don't fill objects, just draw the outline.
|
|
- `tent_vias`: [boolean=true] Cover the vias.
|
|
- `uppercase_extensions`: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `width_adjust`: [number=0] This width factor is intended to compensate PS printers/plotters that do not strictly obey line width settings.
|
|
Only used to plot pads and tracks.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* QR_Lib
|
|
* Type: `qr_lib`
|
|
* Description: Generates a QR code symbol and footprint.
|
|
This output creates a library containing a symbol and footprint for a QR code.
|
|
To refresh the generated symbols and footprints use the `update_qr` preflight.
|
|
The workflow is as follows:
|
|
- Create the symbol and footprints using this output.
|
|
- Use them in your schematic and PCB.
|
|
- To keep them updated add the `update_qr` preflight
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `boardview` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`lib`**: [string='QR'] Short name for the library.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=qr, %x=lib). Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`qrs`**: [list(dict)] QR codes to include in the library.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`layer`**: [string='silk'] [silk,copper] Layer for the footprint.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string='QR'] Name for the symbol/footprint.
|
|
- **`size_pcb`**: [number=15] Size of the QR footprint.
|
|
- **`size_sch`**: [number=15] Size of the QR symbol.
|
|
- **`text`**: [string='%p %r'] Text to encode as QR.
|
|
- `correction_level`: [string='low'] [low,medium,quartile,high] Error correction level.
|
|
- `pcb_negative`: [boolean=false] Generate a negative image for the PCB.
|
|
- `size_units`: [string='millimeters'] [millimeters,inches] Units used for the size.
|
|
- `reference`: [string='QR'] The reference prefix.
|
|
- `use_sch_dir`: [boolean=true] Generate the libs relative to the schematic/PCB dir.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=90] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* 3D render of the PCB
|
|
* Type: `render_3d`
|
|
* Description: Exports the image generated by KiCad's 3D viewer.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `render_3d` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`download`**: [boolean=true] Downloads missing 3D models from KiCad git. Only applies to models in KISYS3DMOD.
|
|
- **`move_x`**: [number=0] Steps to move in the X axis, positive is to the right.
|
|
Just like pressing the right arrow in the 3D viewer.
|
|
- **`move_y`**: [number=0] Steps to move in the Y axis, positive is up.
|
|
Just like pressing the up arrow in the 3D viewer.
|
|
- **`no_virtual`**: [boolean=false] Used to exclude 3D models for components with 'virtual' attribute.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the generated image file (%i='3D_$VIEW' %x='png'). Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`ray_tracing`**: [boolean=false] Enable the ray tracing. Much better result, but slow, and you'll need to adjust `wait_rt`.
|
|
- **`rotate_x`**: [number=0] Steps to rotate around the X axis, positive is clockwise.
|
|
Each step is currently 10 degrees. Only for KiCad 6.
|
|
- **`rotate_y`**: [number=0] Steps to rotate around the Y axis, positive is clockwise.
|
|
Each step is currently 10 degrees. Only for KiCad 6.
|
|
- **`rotate_z`**: [number=0] Steps to rotate around the Z axis, positive is clockwise.
|
|
Each step is currently 10 degrees. Only for KiCad 6.
|
|
- **`view`**: [string='top'] [top,bottom,front,rear,right,left,z,Z,y,Y,x,X] Point of view.
|
|
- **`zoom`**: [number=0] Zoom steps. Use positive to enlarge, get closer, and negative to reduce.
|
|
Same result as using the mouse wheel in the 3D viewer.
|
|
- `background1`: [string='#66667F'] First color for the background gradient.
|
|
- `background2`: [string='#CCCCE5'] Second color for the background gradient.
|
|
- `board`: [string='#332B16'] Color for the board without copper or solder mask.
|
|
- `clip_silk_on_via_annulus`: [boolean=true] Clip silkscreen at via annuli (KiCad 6).
|
|
- `copper`: [string='#8b898c'] Color for the copper.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `height`: [number=720] Image height (aprox.).
|
|
- `kicad_3d_url`: [string='https://gitlab.com/kicad/libraries/kicad-packages3D/-/raw/master/'] Base URL for the KiCad 3D models.
|
|
- `no_smd`: [boolean=false] Used to exclude 3D models for surface mount components.
|
|
- `no_tht`: [boolean=false] Used to exclude 3D models for through hole components.
|
|
- `orthographic`: [boolean=false] Enable the orthographic projection mode (top view looks flat).
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `show_silkscreen`: [boolean=true] Show the silkscreen layers (KiCad 6).
|
|
- `show_soldermask`: [boolean=true] Show the solder mask layers (KiCad 6).
|
|
- `show_solderpaste`: [boolean=true] Show the solder paste layers (KiCad 6).
|
|
- `show_zones`: [boolean=true] Show filled areas in zones (KiCad 6).
|
|
- `silk`: [string='#d5dce4'] Color for the silk screen.
|
|
- `solder_mask`: [string='#208b47'] Color for the solder mask.
|
|
- `solder_paste`: [string='#808080'] Color for the solder paste.
|
|
- `subtract_mask_from_silk`: [boolean=true] Clip silkscreen at solder mask edges (KiCad 6).
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- *wait_ray_tracing*: Alias for wait_render.
|
|
- `wait_render`: [number=-600] How many seconds we must wait before capturing the render (ray tracing or normal).
|
|
Lamentably KiCad can save an unfinished image. Enlarge it if your image looks partially rendered.
|
|
Use negative values to enable the auto-detect using CPU load.
|
|
In this case the value is interpreted as a time-out..
|
|
- `width`: [number=1280] Image width (aprox.).
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Design report
|
|
* Type: `report`
|
|
* Description: Generates a report about the design.
|
|
Mainly oriented to be sent to the manufacturer or check PCB details.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `report` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`convert_to`**: [string='pdf'] Target format for the report conversion. See `do_convert`.
|
|
- **`do_convert`**: [boolean=false] Run `Pandoc` to convert the report. Note that Pandoc must be installed.
|
|
The conversion is done assuming the report is in `convert_from` format.
|
|
The output file will be in `convert_to` format.
|
|
The available formats depends on the `Pandoc` installation.
|
|
In CI/CD environments: the `kicad_auto_test` docker image contains it.
|
|
In Debian/Ubuntu environments: install `pandoc`, `texlive-latex-base` and `texlive-latex-recommended`.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name (%i='report', %x='txt'). Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`template`**: [string='full'] Name for one of the internal templates (full, full_svg, simple) or a custom template file.
|
|
Environment variables and ~ are allowed.
|
|
Note: when converting to PDF PanDoc can fail on some Unicode values (use `simple_ASCII`).
|
|
- `convert_from`: [string='markdown'] Original format for the report conversion. Current templates are `markdown`. See `do_convert`.
|
|
- `converted_output`: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Converted output file name (%i='report', %x=`convert_to`).
|
|
Note that the extension should match the `convert_to` value. Affected by global options.
|
|
- `eurocircuits_class_target`: [string='10F'] Which Eurocircuits class are we aiming at.
|
|
- `eurocircuits_reduce_holes`: [number=0.45] When computing the Eurocircuits category: Final holes sizes smaller or equal to this given
|
|
diameter can be reduced to accommodate the correct annular ring values.
|
|
Use 0 to disable it.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* Schematic with variant generator
|
|
* Type: `sch_variant`
|
|
* Description: Creates a copy of the schematic with all the filters and variants applied.
|
|
This copy isn't intended for development.
|
|
Is just a tweaked version of the original where you can look at the results.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `sch_variant` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `copy_project`: [boolean=false] Copy the KiCad project to the destination directory.
|
|
Disabled by default for compatibility with older versions.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `title`: [string=''] Text used to replace the sheet title. %VALUE expansions are allowed.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the text is concatenated.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* STEP (ISO 10303-21 Clear Text Encoding of the Exchange Structure)
|
|
* Type: `step`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB as a 3D model.
|
|
This is the most common 3D format for exchange purposes.
|
|
This output is what you get from the 'File/Export/STEP' menu in pcbnew.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `step` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`download`**: [boolean=true] Downloads missing 3D models from KiCad git. Only applies to models in KISYS3DMOD.
|
|
- **`no_virtual`**: [boolean=false] Used to exclude 3D models for components with 'virtual' attribute.
|
|
- **`origin`**: [string='grid'] Determines the coordinates origin. Using grid the coordinates are the same as you have in the design sheet.
|
|
The drill option uses the auxiliary reference defined by the user.
|
|
You can define any other origin using the format 'X,Y', i.e. '3.2,-10'.
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the generated STEP file (%i='3D' %x='step'). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `kicad_3d_url`: [string='https://gitlab.com/kicad/libraries/kicad-packages3D/-/raw/master/'] Base URL for the KiCad 3D models.
|
|
- `metric_units`: [boolean=true] Use metric units instead of inches.
|
|
- `min_distance`: [number=-1] The minimum distance between points to treat them as separate ones (-1 is KiCad default: 0.01 mm).
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `subst_models`: [boolean=true] Substitute STEP or IGS models with the same name in place of VRML models.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics)
|
|
* Type: `svg`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB to a format suitable for 2D graphics software.
|
|
Unlike bitmaps SVG drawings can be scaled without losing resolution.
|
|
This output is what you get from the File/Plot menu in pcbnew.
|
|
The `pcb_print` is usually a better alternative.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`layers`**: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user]
|
|
List of PCB layers to plot.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `description`: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `layer`: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad.
|
|
- `suffix`: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `svg` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty.
|
|
IMPORTANT! KiCad will always create the file using its own name and then we can rename it.
|
|
For this reason you must avoid generating two variants at the same directory when one of
|
|
them uses the default KiCad name. Affected by global options.
|
|
- **`plot_sheet_reference`**: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result
|
|
(i.e. always the default worksheet style, also problems expanding text variables).
|
|
The `pcb_print` output can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs.
|
|
- `custom_reports`: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `content`: [string=''] Content for the report. Use ${basename} for the project name without extension.
|
|
Use ${filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER.
|
|
- `output`: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `drill_marks`: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale).
|
|
- `edge_cut_extension`: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot.
|
|
- `exclude_edge_layer`: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer.
|
|
- `exclude_pads_from_silkscreen`: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only).
|
|
- `force_plot_invisible_refs_vals`: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible.
|
|
- `inner_extension_pattern`: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers.
|
|
The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number.
|
|
Example '.g%n'.
|
|
- `line_width`: [number=0.25] [0.02,2] For objects without width [mm] (KiCad 5).
|
|
- `mirror_plot`: [boolean=false] Plot mirrored.
|
|
- `negative_plot`: [boolean=false] Invert black and white.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_refs`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references.
|
|
- `plot_footprint_values`: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `tent_vias`: [boolean=true] Cover the vias.
|
|
- `uppercase_extensions`: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* SVG PCB Print (Scalable Vector Graphics)
|
|
* Type: `svg_pcb_print`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB to the scalable vector graphics format.
|
|
This output is what you get from the 'File/Print' menu in pcbnew.
|
|
The `pcb_print` is usually a better alternative.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`layers`**: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user]
|
|
List of PCB layers to include in the PDF.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- `description`: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes.
|
|
- `layer`: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad.
|
|
- `suffix`: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `pdf_pcb_print` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`output`**: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output SVG (%i=layers, %x=svg). Affected by global options.
|
|
- *output_name*: Alias for output.
|
|
- **`plot_sheet_reference`**: [boolean=true] Include the title-block.
|
|
- **`scaling`**: [number=1.0] Scale factor (0 means autoscaling). You should disable `plot_sheet_reference` when using it.
|
|
- **`separated`**: [boolean=false] Print layers in separated pages.
|
|
- `color_theme`: [string='_builtin_classic'] Selects the color theme. Onlyu applies to KiCad 6.
|
|
To use the KiCad 6 default colors select `_builtin_default`.
|
|
Usually user colors are stored as `user`, but you can give it another name.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `drill_marks`: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale).
|
|
- `enable_ki5_page_fix`: [boolean=true] Enable workaround for KiCad 5 bug.
|
|
- `enable_ki6_page_fix`: [boolean=true] Enable workaround for KiCad 6 bug #11033.
|
|
- `force_edge_cuts`: [boolean=true] Only useful for KiCad 6 when printing in one page, you can disable the edge here.
|
|
KiCad 5 forces it by default, and you can't control it from config files.
|
|
Same for KiCad 6 when printing to separated pages.
|
|
- `hide_excluded`: [boolean=false] Hide components in the Fab layer that are marked as excluded by a variant.
|
|
Affected by global options.
|
|
- `mirror`: [boolean=false] Print mirrored (X axis inverted). ONLY for KiCad 6.
|
|
- `monochrome`: [boolean=false] Print in black and white.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `title`: [string=''] Text used to replace the sheet title. %VALUE expansions are allowed.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the text is concatenated.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
* SVG Schematic Print
|
|
* Type: `svg_sch_print`
|
|
* Description: Exports the PCB. Suitable for printing.
|
|
This is a format to document your schematic.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`comment`**: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.
|
|
- **`dir`**: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files.
|
|
If it starts with `+` the rest is concatenated to the default dir.
|
|
- **`name`**: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition.
|
|
- **`options`**: [dict] Options for the `svg_sch_print` output.
|
|
* Valid keys:
|
|
- **`frame`**: [boolean=true] Include the frame and title block.
|
|
- `all_pages`: [boolean=true] Generate with all hierarchical sheets.
|
|
- `dnf_filter`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `monochrome`: [boolean=false] Generate a monochromatic PDF.
|
|
- `output`: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output SVG (%i=schematic, %x=svg). Affected by global options.
|
|
- `pre_transform`: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to transform fields before applying other filters.
|
|
A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill.
|
|
- `variant`: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
|
|
Not fitted components are crossed.
|
|
- `category`: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used.
|
|
Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber.
|
|
- `disable_run_by_default`: [string|boolean] Use it to disable the `run_by_default` status of other output.
|
|
Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original.
|
|
Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending.
|
|
- `extends`: [string=''] Copy the `options` section from the indicated output.
|
|
- `output_id`: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output.
|
|
- `priority`: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first.
|
|
Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs.
|
|
- `run_by_default`: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Consolidating BoMs
|
|
|
|
Some times your project is composed by various boards, other times you are producing various products at the same time.
|
|
In both cases you would want to consolidate the components acquisition in one operation.
|
|
Of course you can create individual BoMs for each project in CSV format and then consolidate them using a spreadsheet editor.
|
|
But KiBot offers another option: you create a BoM for your main project and then aggregate the components from the other projects.
|
|
|
|
Here is a simple example. Suppose you have three projects: *merge_1*, *merge_2* and *merge_3*.
|
|
For the *merge_1* project you could use the following output:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
kibot:
|
|
version: 1
|
|
|
|
outputs:
|
|
- name: 'bom_csv'
|
|
comment: "Bill of Materials in CSV format"
|
|
type: bom
|
|
dir: BoM
|
|
options:
|
|
use_alt: true
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Using the `tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_1.sch` from the git repo and storing the above example in `m1.kibot.yaml` you could run:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
src/kibot -c m1.kibot.yaml -e tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_1.sch -d test_merge
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
And get `test_merge/BoM/merge_1-bom.csv`:
|
|
|
|
| Row | Description | Part | References | Value | Footprint | Quantity Per PCB | Status | Datasheet |
|
|
|--------------------|-----------------------------------|------|------------|-------|-----------|------------------|--------|-----------|
|
|
| 1 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | C1 | 1nF | | 1 | | ~ |
|
|
| 2 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | C2 | 10nF | | 1 | | ~ |
|
|
| 3 | Resistor | R | R1-R3 | 1k | | 3 | | ~ |
|
|
|
|
| Project info: | |
|
|
|--------------------|-----------------------------------|
|
|
| Schematic: | merge_1 |
|
|
| Variant: | default |
|
|
| Revision: | |
|
|
| Date: | 2021-02-02_12-12-27 |
|
|
| KiCad Version: | 5.1.9-73d0e3b20d\~88\~ubuntu21.04.1 |
|
|
| Statistics: | |
|
|
| Component Groups: | 3 |
|
|
| Component Count: | 5 |
|
|
| Fitted Components: | 5 |
|
|
| Number of PCBs: | 1 |
|
|
| Total Components: | 5 |
|
|
|
|
This CSV says you have five components groped in three different types.
|
|
They are one 1 nF capacitor, one 10 nF capacitor and three 1 k resistors.
|
|
Now lets generate BoMs for the *merge_2* example:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
src/kibot -c m1.kibot.yaml -e tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_2.sch -d test_merge
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
We'll get `test_merge/BoM/merge_2-bom.csv`:
|
|
|
|
| Row | Description | Part | References | Value | Footprint | Quantity Per PCB | Status | Datasheet |
|
|
|--------------------|-----------------------------------|------|------------|-------|-----------|------------------|--------|-----------|
|
|
| 1 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | C2 | 1nF | | 1 | | ~ |
|
|
| 2 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | C1 | 10nF | | 1 | | ~ |
|
|
| 3 | Resistor | R | R2-R4 | 1000 | | 3 | | ~ |
|
|
| 4 | Resistor | R | R1 | 10k | | 1 | | ~ |
|
|
|
|
| Project info: | |
|
|
|--------------------|-----------------------------------|
|
|
| Schematic: | merge_2 |
|
|
| Variant: | default |
|
|
| Revision: | |
|
|
| Date: | 2021-01-27_10-19-46 |
|
|
| KiCad Version: | 5.1.9-73d0e3b20d\~88\~ubuntu21.04.1 |
|
|
| Statistics: | |
|
|
| Component Groups: | 4 |
|
|
| Component Count: | 6 |
|
|
| Fitted Components: | 6 |
|
|
| Number of PCBs: | 1 |
|
|
| Total Components: | 6 |
|
|
|
|
In this project we have six components from four different types.
|
|
They are similar to *merge_1* but now we also have a 10 k resistor.
|
|
We don't need to generate this BoM to consolidate our projects, but is good to know what we have.
|
|
And now lets generate BoMs for the *merge_3* example:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
src/kibot -c m1.kibot.yaml -e tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_3.sch -d test_merge
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
We'll get `test_merge/BoM/merge_3-bom.csv`:
|
|
|
|
| Row | Description | Part | References | Value | Footprint | Quantity Per PCB | Status | Datasheet |
|
|
|--------------------|-----------------------------------|------|------------|-------|-----------|------------------|--------|-----------|
|
|
| 1 | Resistor | R | R5 | 1k | | 1 | | ~ |
|
|
| 2 | Resistor | R | R1-R4 | 10k | | 4 | | ~ |
|
|
|
|
| Project info: | |
|
|
|--------------------|-----------------------------------|
|
|
| Schematic: | merge_3 |
|
|
| Variant: | default |
|
|
| Revision: | |
|
|
| Date: | 2021-01-27_10-21-29 |
|
|
| KiCad Version: | 5.1.9-73d0e3b20d\~88\~ubuntu21.04.1 |
|
|
| Statistics: | |
|
|
| Component Groups: | 2 |
|
|
| Component Count: | 5 |
|
|
| Fitted Components: | 5 |
|
|
| Number of PCBs: | 1 |
|
|
| Total Components: | 5 |
|
|
|
|
This time we also have five components, but from two different types.
|
|
They are one 1 k resistor and four 10 k resistors.
|
|
Now suppose we want to create 10 boards for *merge_1*, 20 for *merge_2* and 30 for *merge_3*.
|
|
We could use the following configuration:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
kibot:
|
|
version: 1
|
|
|
|
outputs:
|
|
- name: 'bom_csv'
|
|
comment: "Bill of Materials in CSV format"
|
|
type: bom
|
|
dir: BoM
|
|
options:
|
|
use_alt: true
|
|
number: 10
|
|
aggregate:
|
|
- file: tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_2.sch
|
|
number: 20
|
|
- file: tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_3.sch
|
|
number: 30
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Save it as `m2.kibot.yaml` and run:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
src/kibot -c m2.kibot.yaml -e tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_1.sch -d test_merge_consolidate
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The `test_merge_consolidate/BoM/merge_1-bom.csv` file will be generated containing:
|
|
|
|
| Row | Description | Part | References | Value | Footprint | Quantity Per PCB | Build Quantity | Status | Datasheet | Source BoM |
|
|
|--------------------|-----------------------------------|------|----------------|-------|-----------|------------------|----------------|--------|-----------|----------------------------------|
|
|
| 1 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | C1 C2 | 1nF | | 2 | 30 | | ~ | merge_1(1) merge_2(1) |
|
|
| 2 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | C2 C1 | 10nF | | 2 | 30 | | ~ | merge_1(1) merge_2(1) |
|
|
| 3 | Resistor | R | R1-R3 R2-R4 R5 | 1k | | 7 | 120 | | ~ | merge_1(3) merge_2(3) merge_3(1) |
|
|
| 4 | Resistor | R | R1 R1-R4 | 10k | | 5 | 140 | | ~ | merge_2(1) merge_3(4) |
|
|
|
|
| Project info: | |
|
|
|--------------------|-----------------------------------|
|
|
| Variant: | default |
|
|
| KiCad Version: | 5.1.9-73d0e3b20d\~88\~ubuntu21.04.1 |
|
|
| Global statistics: | |
|
|
| Component Groups: | 4 |
|
|
| Component Count: | 16 |
|
|
| Fitted Components: | 16 |
|
|
| Number of PCBs: | 60 |
|
|
| Total Components: | 320 |
|
|
| Project info: | merge_1 |
|
|
| Schematic: | merge_1 |
|
|
| Revision: | |
|
|
| Date: | 2021-02-02_12-12-27 |
|
|
| Company: | Test company |
|
|
| Statistics: | merge_1 |
|
|
| Component Groups: | 3 |
|
|
| Component Count: | 5 |
|
|
| Fitted Components: | 5 |
|
|
| Number of PCBs: | 10 |
|
|
| Total Components: | 50 |
|
|
| Project info: | merge_2 |
|
|
| Schematic: | merge_2 |
|
|
| Revision: | |
|
|
| Date: | 2021-01-27_10-19-46 |
|
|
| Statistics: | merge_2 |
|
|
| Component Groups: | 4 |
|
|
| Component Count: | 6 |
|
|
| Fitted Components: | 6 |
|
|
| Number of PCBs: | 20 |
|
|
| Total Components: | 120 |
|
|
| Project info: | merge_3 |
|
|
| Schematic: | merge_3 |
|
|
| Revision: | |
|
|
| Date: | 2021-01-27_10-21-29 |
|
|
| Statistics: | merge_3 |
|
|
| Component Groups: | 2 |
|
|
| Component Count: | 5 |
|
|
| Fitted Components: | 5 |
|
|
| Number of PCBs: | 30 |
|
|
| Total Components: | 150 |
|
|
|
|
You can see that now we have much more stats.
|
|
They say we have four different types, thirteen for board sets, a total of 60 boards and 250 components.
|
|
Then we have individual stats for each project.
|
|
The capacitors are easy to interpret, we have 30 1 nF capacitors *merge_1* project has one and *merge_2* another.
|
|
As we have 10 *merge_1* and 20 *merge_2* boards this is clear.
|
|
But looking at the 1 k resistors is harder. We have 80, three from *merge_1*, one from *merge_2* and another from *merge_3*.
|
|
So we have 10*3+20*3+30=120, this is clear, but the BoM says they are R1-R3 R2-R4 R5, which is a little bit confusing.
|
|
In this simple example is easy to correlate R1-R3 to *merge_1*, R2-R4 to *merge_2* and R5 to *merge_1*.
|
|
For bigger projects this gets harder.
|
|
Lets assign an *id* to each project, we'll use 'A' for *merge_1*, 'B' for *merge_2* and 'C' for *merge_3*:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
kibot:
|
|
version: 1
|
|
|
|
outputs:
|
|
- name: 'bom_csv'
|
|
comment: "Bill of Materials in CSV format"
|
|
type: bom
|
|
dir: BoM
|
|
options:
|
|
use_alt: true
|
|
number: 10
|
|
ref_id: 'A:'
|
|
aggregate:
|
|
- file: tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_2.sch
|
|
number: 20
|
|
ref_id: 'B:'
|
|
- file: tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_3.sch
|
|
number: 30
|
|
ref_id: 'C:'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Now `test_merge_consolidate/BoM/merge_1-bom.csv` will have the following information:
|
|
|
|
| Row | Description | Part | References | Value | Footprint | Quantity Per PCB | Build Quantity | Status | Datasheet | Source BoM |
|
|
|-----|-----------------------|------|--------------------------|-------|-----------|------------------|----------------|--------|-----------|----------------------------------|
|
|
| 1 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | A:C1 B:C2 | 1nF | | 2 | 30 | | ~ | merge_1(1) merge_2(1) |
|
|
| 2 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | A:C2 B:C1 | 10nF | | 2 | 30 | | ~ | merge_1(1) merge_2(1) |
|
|
| 3 | Resistor | R | A:R1-A:R3 B:R2-B:R4 C:R5 | 1k | | 7 | 120 | | ~ | merge_1(3) merge_2(3) merge_3(1) |
|
|
| 4 | Resistor | R | B:R1 C:R1-C:R4 | 10k | | 5 | 140 | | ~ | merge_2(1) merge_3(4) |
|
|
|
|
As you can see now we know `A` has R1-R3, `B` R2-R4 and for `C` R5 is the 1k resistor.
|
|
If we want to compact the `Source BoM` column we just need to enable the `source_by_id` option:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
kibot:
|
|
version: 1
|
|
|
|
outputs:
|
|
- name: 'bom_csv'
|
|
comment: "Bill of Materials in CSV format"
|
|
type: bom
|
|
dir: BoM
|
|
options:
|
|
use_alt: true
|
|
number: 10
|
|
ref_id: 'A:'
|
|
source_by_id: true
|
|
aggregate:
|
|
- file: tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_2.sch
|
|
number: 20
|
|
ref_id: 'B:'
|
|
- file: tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_3.sch
|
|
number: 30
|
|
ref_id: 'C:'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
And we'll get:
|
|
|
|
| Row | Description | Part | References | Value | Footprint | Quantity Per PCB | Build Quantity | Status | Datasheet | Source BoM |
|
|
|-----|-----------------------|------|--------------------------|-------|-----------|------------------|----------------|--------|-----------|-------------------|
|
|
| 1 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | A:C1 B:C2 | 1nF | | 2 | 30 | | ~ | A:(1) B:(1) |
|
|
| 2 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | A:C2 B:C1 | 10nF | | 2 | 30 | | ~ | A:(1) B:(1) |
|
|
| 3 | Resistor | R | A:R1-A:R3 B:R2-B:R4 C:R5 | 1k | | 7 | 120 | | ~ | A:(3) B:(3) C:(1) |
|
|
| 4 | Resistor | R | B:R1 C:R1-C:R4 | 10k | | 5 | 140 | | ~ | B:(1) C:(4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Importing outputs from another file
|
|
|
|
In some cases you may want to reuse configuration files. An example of this are the example files that generate gerbers and drill files for various manufacturers ([see](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/tree/master/docs/samples)).
|
|
|
|
In this case you can create a section named `import` containing a list of configuration files. Here is an example:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
import:
|
|
- configs/Elecrow.kibot.yaml
|
|
- configs/FusionPCB.kibot.yaml
|
|
- configs/JLCPCB.kibot.yaml
|
|
- configs/P-Ban.kibot.yaml
|
|
- configs/PCBWay.kibot.yaml
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This will import all the outputs from the listed files.
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Using other output as base for a new one
|
|
|
|
If you need to define an output that is similar to another, and you want to avoid copying the options from the former, you can *extend* an output.
|
|
To achieve it just specify the name of the base output in the `extends` value.
|
|
Note that this will use the `options` of the other output as base, not other data as the comment.
|
|
|
|
Also note that you can use YAML anchors, but this won't work if you are importing the base output from other file.
|
|
|
|
Additionally you must be aware that extending an output doesn't disable the base output.
|
|
If you need to disable the original output use `disable_run_by_default` option.
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Importing filters and variants from another file
|
|
|
|
This is a more complex case of the previous [Importing outputs from another file](#importing-outputs-from-another-file).
|
|
In this case you must use the more general syntax:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
import:
|
|
- file: FILE_CONTAINING_THE_YAML_DEFINITIONS
|
|
outputs: LIST_OF_OUTPUTS
|
|
preflights: LIST_OF_PREFLIGHTS
|
|
filters: LIST_OF_FILTERS
|
|
variants: LIST_OF_VARIANTS
|
|
global: LIST_OF_GLOBALS
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This syntax is flexible. If you don't define which `outputs`, `filters`, `variants` and/or `global` all will be imported. So you can just omit them, like this:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
import:
|
|
- file: FILE_CONTAINING_THE_YAML_DEFINITIONS
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The `LIST_OF_items` can be a YAML list or just one string. Here is an example:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
import:
|
|
- file: FILE_CONTAINING_THE_YAML_DEFINITIONS
|
|
outputs: one_name
|
|
filters: ['name1', 'name2']
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This will import the `one_name` output and the `name1` and `name2` filters. As `variants` is omitted, all variants will be imported.
|
|
You can also use the `all` and `none` special names, like this:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
import:
|
|
- file: FILE_CONTAINING_THE_YAML_DEFINITIONS
|
|
outputs: all
|
|
filters: all
|
|
variants: none
|
|
global: none
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This will import all outputs and filters, but not variants or globals.
|
|
Also note that imported globals has more precedence than the ones defined in the same file.
|
|
If you want give more priority to the local values use:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
kibot:
|
|
version: 1
|
|
imported_global_has_less_priority: true
|
|
|
|
import:
|
|
...
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Another important detail is that global options that are lists gets the values merged.
|
|
The last set of values found is inserted at the beginning of the list.
|
|
You can collect filters for all the imported global sections.
|
|
|
|
### Doing YAML substitution or preprocessing
|
|
|
|
Sometimes you could want to change values in the YAML depending on external stuff,
|
|
or just want to be able to change something for each variant run.
|
|
|
|
In this case you can use external tools to create various YAML files using a template,
|
|
but you can also use KiBot's definitions.
|
|
|
|
The definitions allows you to replace tags like `@VARIABLE@` by some specified value.
|
|
These definitions can be specified at the command line using the `-E` option.
|
|
As an example: `-E UNITS=millimeters` will replace all `@UNITS@` markers by `millimeters`.
|
|
This is applied to all YAML files loaded, so this propagates to all the imported YAML files.
|
|
|
|
You can use `-E` as many times as you need.
|
|
|
|
## Usage
|
|
|
|
For a quick start just go to the project's dir and run:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot --quick-start
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This will generate a configuration and generate outputs.
|
|
If you want to just generate the configuration, and not the outputs, use:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot --quick-start --dry
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If you need a more exhaustive configuration file try:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot --example
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This will generate a file named `example.kibot.yaml` containing all the available options and comments about them.
|
|
You can use it to create your own configuration file.
|
|
|
|
If you want to use the layers of a particular PCB in the example use:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot -b PCB_FILE --example
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
And if you want to use the same options selected in the plot dialog use:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot -b PCB_FILE -p --example
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If the current directory contains only one PCB file and only one configuration file (named *.kibot.yaml) you can just call `kibot`.
|
|
No arguments needed.
|
|
The tool will figure out which files to use.
|
|
|
|
If more than one file is found in the current directory `kibot` will use the first found and issue a warning.
|
|
If you need to use other file just tell it explicitly:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot -b PCB_FILE.kicad_pcb -c CONFIG.kibot.yaml
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
A simple target can be added to your `makefile`, so you can just run `make pcb_files` or integrate into your current build process.
|
|
|
|
```Makefile
|
|
pcb_files:
|
|
kibot -b $(PCB) -c $(KIBOT_CFG)
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If you need to suppress messages use `--quiet` or `-q` and if you need to get more information about what's going on use `--verbose` or `-v`.
|
|
|
|
If you want to generate only some of the outputs use:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot OUTPUT_1 OUTPUT_2
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If you want to generate all outputs with some exceptions use:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot --invert-sel OUTPUT_1 OUTPUT_2
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Note that you can use the `run_by_default` option of the output you want to exclude from the default runs.
|
|
|
|
If you want to skip the DRC and ERC use:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot --skip-pre run_erc,run_drc
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If you want to skip all the `preflight` tasks use:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot --skip-pre all
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
All outputs are generated using the current directory as base.
|
|
If you want to use another directory as base use:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot --out-dir OTHER_PLACE
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If you want to list the available outputs defined in the configuration file use:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
kibot --list
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Command line help
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
KiBot: KiCad automation tool for documents generation
|
|
|
|
Usage:
|
|
kibot [-b BOARD] [-e SCHEMA] [-c CONFIG] [-d OUT_DIR] [-s PRE] [-D]
|
|
[-q | -v...] [-C | -i | -n] [-m MKFILE] [-A] [-g DEF] ...
|
|
[-E DEF] ... [-w LIST] [TARGET...]
|
|
kibot [-v...] [-b BOARD] [-e SCHEMA] [-c PLOT_CONFIG] [-E DEF] ... --list
|
|
kibot [-v...] [-b BOARD] [-d OUT_DIR] [-p | -P] --example
|
|
kibot [-v...] [--start PATH] [-d OUT_DIR] [--dry] [-t, --type TYPE]...
|
|
--quick-start
|
|
kibot [-v...] --help-filters
|
|
kibot [-v...] [--markdown|--json] --help-dependencies
|
|
kibot [-v...] --help-global-options
|
|
kibot [-v...] --help-list-outputs
|
|
kibot [-v...] --help-output=HELP_OUTPUT
|
|
kibot [-v...] --help-outputs
|
|
kibot [-v...] --help-preflights
|
|
kibot [-v...] --help-variants
|
|
kibot -h | --help
|
|
kibot --version
|
|
|
|
Arguments:
|
|
TARGET Outputs to generate, default is all
|
|
|
|
Options:
|
|
-A, --no-auto-download Disable dependencies auto-download
|
|
-b BOARD, --board-file BOARD The PCB .kicad-pcb board file
|
|
-c CONFIG, --plot-config CONFIG The plotting config file to use
|
|
-C, --cli-order Generate outputs using the indicated order
|
|
-d OUT_DIR, --out-dir OUT_DIR The output directory [default: .]
|
|
-D, --dont-stop Try to continue if an output fails
|
|
-e SCHEMA, --schematic SCHEMA The schematic file (.sch)
|
|
-E DEF, --define DEF Define preprocessor value (VAR=VAL)
|
|
-g DEF, --global-redef DEF Overwrite a global value (VAR=VAL)
|
|
-i, --invert-sel Generate the outputs not listed as targets
|
|
-l, --list List available outputs (in the config file)
|
|
-m MKFILE, --makefile MKFILE Generate a Makefile (no targets created)
|
|
-n, --no-priority Don't sort targets by priority
|
|
-p, --copy-options Copy plot options from the PCB file
|
|
-P, --copy-and-expand As -p but expand the list of layers
|
|
-q, --quiet Remove information logs
|
|
-s PRE, --skip-pre PRE Skip preflights, comma separated or `all`
|
|
-v, --verbose Show debugging information
|
|
-V, --version Show program's version number and exit
|
|
-w, --no-warn LIST Exclude the mentioned warnings (comma sep)
|
|
-x, --example Create a template configuration file
|
|
|
|
Quick start options:
|
|
--quick-start Generates demo config files and their outputs
|
|
--dry Just generate the config files
|
|
--start PATH Starting point for the search [default: .]
|
|
-t, --type TYPE Generate examples only for the indicated type/s
|
|
|
|
Help options:
|
|
-h, --help Show this help message and exit
|
|
--help-dependencies List dependencies in human readable format
|
|
--help-filters List supported filters and details
|
|
--help-global-options List supported global variables
|
|
--help-list-outputs List supported outputs
|
|
--help-output HELP_OUTPUT Help for this particular output
|
|
--help-outputs List supported outputs and details
|
|
--help-preflights List supported preflights and details
|
|
--help-variants List supported variants and details
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Usage for CI/CD
|
|
|
|
When using a GitHub or GitLab repo you can use KiBot to generate all the needed stuff each time you commit a change to the schematic and/or PCB file.
|
|
|
|
If you want a quick demo of what KiBot can do on a GitHub project try the following [workflow](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kibot_variants_arduprog/blob/master/.github/workflows/kibot_quick_start.yml).
|
|
You just need to enable GitHub workflows and copy this workflow to your `.github/workflows/` folder. In this mode KiBot will detect the project files, create a configuration and generate the targets.
|
|
This workflow collects the generated files in `Automatic_outputs.zip`.
|
|
|
|
Examples of how to use KiBot can be found [here for GitHub](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad_ci_test) and [here for GitLab](https://gitlab.com/set-soft/kicad-ci-test).
|
|
|
|
In order to run KiBot on these environments you need a lot of software installed. The usual mechanism to achieve this is using [docker](https://www.docker.com/).
|
|
Docker images containing KiBot, all the supporting scripts and a corresponding KiCad can be found in the
|
|
[kicad5_auto](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad_auto/pkgs/container/kicad5_auto) and
|
|
[kicad6_auto](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad_auto/pkgs/container/kicad6_auto) GitHub packages.
|
|
More complete images, with Pandoc and testing tools, can be found in the following packages:
|
|
[kicad5_auto_full](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad_auto/pkgs/container/kicad5_auto_full) and
|
|
[kicad6_auto_full](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad_auto/pkgs/container/kicad6_auto_full) GitHub packages.
|
|
Old images can be found at [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/) as [setsoft/kicad_auto](https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/setsoft/kicad_auto) and
|
|
[setsoft/kicad_auto_test](https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/setsoft/kicad_auto_test).
|
|
|
|
The images are based on [kicad5_debian](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad_auto/pkgs/container/kicad5_debian) and
|
|
[kicad6_debian](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad_auto/pkgs/container/kicad5_debian)
|
|
([setsoft/kicad_debian](https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/setsoft/kicad_debian) on Docker Hub), containing KiCad on Debian GNU/Linux.
|
|
|
|
If you need to run the current development version of KiBot you can use the following docker images:
|
|
[ghcr.io/inti-cmnb/kicad5_auto:dev](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad_auto/pkgs/container/kicad5_auto) or
|
|
[ghcr.io/inti-cmnb/kicad6_auto:dev](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad_auto/pkgs/container/kicad6_auto)
|
|
([setsoft/kicad_auto:dev](https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/setsoft/kicad_auto)).
|
|
|
|
The most important images are:
|
|
|
|
| Name | KiBot | KiCad |
|
|
| :----------------------------------- | ------------ | ----: |
|
|
| ghcr.io/inti-cmnb/kicad5_auto:latest | last release | 5.1.9 |
|
|
| ghcr.io/inti-cmnb/kicad6_auto:latest | last release | 6.x |
|
|
| ghcr.io/inti-cmnb/kicad5_auto:dev | git code | 5.1.9 |
|
|
| ghcr.io/inti-cmnb/kicad6_auto:dev | git code | 6.x |
|
|
| ghcr.io/inti-cmnb/kicad5_auto:1.2.0 | 1.2.0 | 5.1.9 |
|
|
| ghcr.io/inti-cmnb/kicad6_auto:1.2.0 | 1.2.0 | 6.0.5 |
|
|
|
|
For more information about the docker images visit [kicad_debian](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad_debian) and [kicad_auto](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad_auto).
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Usage of Github Actions
|
|
|
|
Note: You can also use --quick-start functionality with GitHub actions, and example is this [workflow](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kibot_variants_arduprog/blob/master/.github/workflows/kibot_action_quick_start.yml)
|
|
|
|
You need to put a [config.kibot.yaml](#configuration) file into the KiCad project folder.
|
|
|
|
Here is an example of workflow file using the GitHub Action:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
name: example
|
|
|
|
on:
|
|
push:
|
|
paths:
|
|
- '**.sch'
|
|
- '**.kicad_pcb'
|
|
pull_request:
|
|
paths:
|
|
- '**.sch'
|
|
- '**.kicad_pcb'
|
|
|
|
jobs:
|
|
example:
|
|
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
|
steps:
|
|
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
|
- uses: INTI-CMNB/KiBot@v2
|
|
with:
|
|
# Required - kibot config file
|
|
config: config.kibot.yaml
|
|
# optional - prefix to output defined in config
|
|
dir: output
|
|
# optional - schematic file
|
|
schema: 'schematic.sch'
|
|
# optional - PCB design file
|
|
board: 'pcb.kicad_pcb'
|
|
- name: upload results
|
|
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
|
with:
|
|
name: output
|
|
path: output
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
For KiCad 6 use `v2_k6` instead of `v2`.
|
|
These actions use the last KiBot stable release, to use the current development code use `v2_dk6` (KiCad 6) and `v2_d` (KiCad 5).
|
|
|
|
A working example applied to a repo can be found [here](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad-ci-test-spora/tree/test_gh_action)
|
|
([spora_main.yml](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kicad-ci-test-spora/blob/test_gh_action/.github/workflows/spora_main.yml)).
|
|
Another example, but using variants can be found [here](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kibot_variants_arduprog)
|
|
([kibot_action.yml](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kibot_variants_arduprog/blob/master/.github/workflows/kibot_action.yml) for KiCad 6,
|
|
[kibot_action.yml](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/kibot_variants_arduprog/blob/KiCad5/.github/workflows/kibot_action.yml) for KiCad 5)
|
|
|
|
The available options are:
|
|
|
|
- **config**: The KiBot config file to use. The first file that matches `*.kibot.yaml` is used when omitted.
|
|
- **dir**: Output directory for the generated files. The current directory is used when omitted.
|
|
- **board**: Name of the PCB file. The first file that matches `*.kicad_pcb` is used when omitted.
|
|
- **quickstart**: When `YES` ignores all the other options and runs in `--quick-start` mode. No configuration needed.
|
|
- **schema**: Name of the schematic file. The first file that matches `*.*sch` is used when omitted.
|
|
- **skip**: Skip preflights, comma separated or *all*. Nothing is skipped when omitted.
|
|
- **targets**: List of targets to generate separated by spaces. To only run preflights use __NONE__. All targets are generated when omitted.
|
|
- **variant**: Global variant to use. No variant is applied when omitted.
|
|
- **verbose**: Level of verbosity. Valid values are 0, 1, 2 or 3. Default is 0.
|
|
|
|
#### Github Actions tags
|
|
|
|
There are several tags you can choose:
|
|
|
|
| Tag | API | KiBot | KiCad |
|
|
| :---------- | --- | ------------ | ----: |
|
|
| v1 | 1 | 1.2.0 | 5.1.9 |
|
|
| v1_k6 | 1 | 1.2.0 | 6.0.5 |
|
|
| v2_1_2_0 | 2 | 1.2.0 | 5.1.9 |
|
|
| v2_k6_1_2_0 | 2 | 1.2.0 | 6.0.5 |
|
|
| v2_1_3_0 | 2 | 1.3.0 | 5.1.9 |
|
|
| v2_k6_1_3_0 | 2 | 1.3.0 | 6.0.7 |
|
|
| v2 | 2 | last release | 5.1.9 |
|
|
| v2_k6 | 2 | last release | 6.x |
|
|
| v2_d | 2 | git code | 5.1.9 |
|
|
| v2_dk6 | 2 | git code | 6.x |
|
|
|
|
The main differences between API 1 and 2 are:
|
|
|
|
- API 2 adds support for variants and quick-start
|
|
- In API 2 you can select which targets are created
|
|
- In API 1 you must specify the input files, in API 2 can be omitted
|
|
- API 1 supports wildcards in the filenames, API 2 doesn't
|
|
- API 2 supports spaces in the filenames, API 1 doesn't
|
|
|
|
## Contributing
|
|
|
|
If you find KiBot useful please consider contributing to the project. There various ways to contribute.
|
|
Of course donations are welcome ([donate](https://www.paypal.com/donate/?hosted_button_id=K2T86GDTTMRPL)), but there are other ways to contribute:
|
|
|
|
- In general:
|
|
- Your workflow: What's missing in KiBot for your workflow? Comment it in the
|
|
[discussions](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/discussions/categories/missing-in-my-workflow)
|
|
- Configuration for a manufacturer: If you have a configuration known to work for a manufacturer please consider contributing it.
|
|
Even if this is a small manufacurer, this helps to know what are the most common options.
|
|
- Mention KiBot: If your project or company uses KiBot you can mention it, so people know about KiBot.
|
|
Also if you are reporting a KiCad issue, currently KiCad developers doesn't pay much attention to automation details.
|
|
- If you are a Windows/Mac OS X user:
|
|
- If you managed to run it locally consider contributing a tutorial of how to do it.
|
|
- If you run KiBot on CI/CD and want to run it locally: consider investing some time on tests.
|
|
Just comment in the [discussions](https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot/discussions/categories/other-platforms)
|
|
and I'll help you to run tests to adapt the code.
|
|
Now that KiCad 6 uses Python 3 most of KiBot functionality should work on Windows and Mac OS X.
|
|
People is using WSL to run KiBot, but we don't have a tutorial about how to do it.
|
|
- If you use a Linux that isn't derived from Debian:
|
|
- Consider helping to add better support for it. Do you know the name of the packages for the dependencies?
|
|
Do you know how to create a package for your distro?
|
|
- If you are good writing tutorials:
|
|
- Consider writing some tutorial about using KiBot. Some examples:
|
|
- How to start using it
|
|
- How to use filters/variants
|
|
- How to create good BoMs
|
|
- If you know Python:
|
|
- Create a new output: KiBot is modular, creating a new output can be done just using some of the `kibot/out_*` files as template.
|
|
The outputs works as plugins and they are automatically discovered by KiBot. Note that you can add them to `~/.config/kibot/plugins`
|
|
- Add regression tests: If you know about Python testing you can add tests to `tests/test_plot/`. We try to cover 100% of the code.
|
|
Even simple tests that check the code executes are welcome.
|
|
- If you know HTML/CSS:
|
|
- Internal BoM styles: You can just take a look at the generated HTMLs and contribute a CSS, or take a look at the code
|
|
(`kibot/bom/html_writer.py`) and add more functionality.
|
|
- Navigate results styles: Similar to the above but for the `navigate_results` output (`kibot/out_navigate_results.py`).
|
|
- If you have drawing skills:
|
|
- Navigate results icons: Currently we have only one set of icons, they are from KiCad 6. Alternative icons are welcome.
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Notes about Gerber format
|
|
|
|
I found this topic poorly documented and quite complex. So here is what I know, feel free to send me any corrections.
|
|
Note that this is a very dynamic topic and this text was written in november 2020.
|
|
|
|
The gerber format is controlled by [Ucamco](https://www.ucamco.com/en/), a leading manufacturer of equipment and software for PCB fabrication.
|
|
Even when this isn't an open standard they release the spec for free and interact with Jean-Pierre Charras (father of KiCad).
|
|
So KiCad support for gerber format is really updated.
|
|
|
|
The gerber format evolved with time, here are the versions I know:
|
|
|
|
* **RS-274D** obsolete version of the format.
|
|
* **RS-274X** (aka **X1**) this is the *extended* version of the format. Is the most widely supported, but has some limitations.
|
|
* **X2** this is the format currently recommended by Ucamco and the default for modern KiCad versions.
|
|
This extension adds important meta-data to the files. It helps CAM operators to know what's every drawing in the image.
|
|
So you know which are pads, tracks, etc. And also more interesting information: impedance controlled tracks, the role of each file, etc.
|
|
Using X2 you can know what is each file without the need of special names or file extensions.
|
|
KiCad can generate drill files using X2.
|
|
* **X3** this is the current draft. One interesting addition is the *Components* role.
|
|
These files replaces the position files, adding important information about the footprint.
|
|
|
|
In addition to them is the spec for the **Gerber Job** file. This file was introduced between X2 and X3, and is used to group all the gerber files.
|
|
The *gbrjob* file contains all the missing stack-up information.
|
|
|
|
KiCad 5 can generate X1, X2 and gerber job files, including drill information in gerber format.
|
|
KiCad 5.99 (6.0 pre-release) can also generate X3 files (position files in gerber format).
|
|
|
|
As you can see the idea of Ucamco is to unify all fabrication information in one format.
|
|
|
|
The **X2** format was designed in a way that software that fully implement **X1** can just ignore the added meta-data.
|
|
In an ideal world you shouldn't bother about it and generate **X2** files. Just use the **gbr** file extension and a *gbrjob* file.
|
|
The problem is with poorly implemented CAM tools. In particular **CAM350**, used by various important cheap China manufacturers.
|
|
This software has known issues interpretating aperture macros and some X2 data.
|
|
If your manufacturer has problems with your files check the following:
|
|
|
|
* Put gerber, drill and position files in the same directory.
|
|
* Disable **X2** extensions (`use_gerber_x2_attributes` set to `false`)
|
|
* Use arcaic role mechanism (`use_protel_extensions` set to `true`)
|
|
* Disable **aperture macros** (KiCad 6 only: `disable_aperture_macros` set to `true`)
|
|
|
|
The [kicad-gerberzipper](https://github.com/g200kg/kicad-gerberzipper) is an action plugin for KiCad oriented to help to generate gerber and drill files for some manufacturers.
|
|
I adapted the configurations from kicad-gerberzipper to KiBot configurations, you can find them in the `docs/samples/` directory.
|
|
They include support for:
|
|
|
|
- [Elecrow](https://www.elecrow.com/)
|
|
- [FusionPCB](https://www.seeedstudio.io/fusion.html)
|
|
- [JLCPCB](https://jlcpcb.com/)
|
|
- [P-Ban](https://www.p-ban.com/)
|
|
- [PCBWay](https://www.pcbway.com)
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Notes about the position file
|
|
|
|
Position files are quite simple. You can generate them as plain text (ASCII) or as a spreadsheet (CSV).
|
|
|
|
But some conventions can make them tricky. Some manufacturers, like [JLCPCB](https://jlcpcb.com/), uses conventions that are incompatible with KiCad.
|
|
|
|
The [following blog](https://dubiouscreations.com/2019/10/21/using-kicad-with-jlcpcb-assembly-service/) explains how to adapt the position files generated by KiCad to what JLCPCB needs.
|
|
To achieve it the author uses a script called [JLCKicadTools](https://github.com/matthewlai/JLCKicadTools).
|
|
|
|
You can achieve the same using KiBot. Here is a configuration example that generates the BoM and position files in the same way JLCKicadTools does:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
kibot:
|
|
version: 1
|
|
|
|
filters:
|
|
- name: only_jlc_parts
|
|
comment: 'Only parts with JLC code'
|
|
type: generic
|
|
include_only:
|
|
- column: 'LCSC#'
|
|
regex: '^C\d+'
|
|
|
|
variants:
|
|
- name: rotated
|
|
comment: 'Just a place holder for the rotation filter'
|
|
type: kibom
|
|
variant: rotated
|
|
pre_transform: _rot_footprint
|
|
|
|
outputs:
|
|
- name: 'position'
|
|
comment: "Pick and place file, JLC style"
|
|
type: position
|
|
options:
|
|
variant: rotated
|
|
output: '%f_cpl_jlc.%x'
|
|
format: CSV
|
|
units: millimeters
|
|
separate_files_for_front_and_back: false
|
|
only_smd: true
|
|
columns:
|
|
- id: Ref
|
|
name: Designator
|
|
- Val
|
|
- Package
|
|
- id: PosX
|
|
name: "Mid X"
|
|
- id: PosY
|
|
name: "Mid Y"
|
|
- id: Rot
|
|
name: Rotation
|
|
- id: Side
|
|
name: Layer
|
|
|
|
- name: 'bom'
|
|
comment: "BoM for JLC"
|
|
type: bom
|
|
options:
|
|
output: '%f_%i_jlc.%x'
|
|
exclude_filter: 'only_jlc_parts'
|
|
ref_separator: ','
|
|
columns:
|
|
- field: Value
|
|
name: Comment
|
|
- field: References
|
|
name: Designator
|
|
- Footprint
|
|
- field: 'LCSC#'
|
|
name: 'LCSC Part #'
|
|
csv:
|
|
hide_pcb_info: true
|
|
hide_stats_info: true
|
|
quote_all: true
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The `only_jlc_parts` filter is used to generate the BoM and assumes you put the JLC component code in a field named `LCSC#` (JLC uses [LCSC](https://lcsc.com/) as supplier).
|
|
Note that the author of the blog simply used `Field4` for this and his script searches for any field containing the `^C\d+` pattern.
|
|
I think this isn't a good idea and I suggest using a defined name, like in this example.
|
|
|
|
The `rotated` variant is used only to apply the `_rot_footprint` transformation filter. This filter is an internal filter of type `rot_footprint`.
|
|
Here is the same configuration file making explicit use of the rotation filter:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
kibot:
|
|
version: 1
|
|
|
|
filters:
|
|
- name: fix_rotation
|
|
comment: 'Adjust rotation for JLC'
|
|
type: rot_footprint
|
|
|
|
- name: only_jlc_parts
|
|
comment: 'Only parts with JLC code'
|
|
type: generic
|
|
include_only:
|
|
- column: 'LCSC#'
|
|
regex: '^C\d+'
|
|
|
|
variants:
|
|
- name: rotated
|
|
comment: 'Just a place holder for the rotation filter'
|
|
type: kibom
|
|
variant: rotated
|
|
pre_transform: fix_rotation
|
|
|
|
outputs:
|
|
- name: 'position'
|
|
comment: "Pick and place file, JLC style"
|
|
type: position
|
|
options:
|
|
variant: rotated
|
|
output: '%f_cpl_jlc.%x'
|
|
format: CSV
|
|
units: millimeters
|
|
separate_files_for_front_and_back: false
|
|
only_smd: true
|
|
columns:
|
|
- id: Ref
|
|
name: Designator
|
|
- Val
|
|
- Package
|
|
- id: PosX
|
|
name: "Mid X"
|
|
- id: PosY
|
|
name: "Mid Y"
|
|
- id: Rot
|
|
name: Rotation
|
|
- id: Side
|
|
name: Layer
|
|
|
|
- name: 'bom'
|
|
comment: "BoM for JLC"
|
|
type: bom
|
|
options:
|
|
output: '%f_%i_jlc.%x'
|
|
exclude_filter: 'only_jlc_parts'
|
|
ref_separator: ','
|
|
columns:
|
|
- field: Value
|
|
name: Comment
|
|
- field: References
|
|
name: Designator
|
|
- Footprint
|
|
- field: 'LCSC#'
|
|
name: 'LCSC Part #'
|
|
csv:
|
|
hide_pcb_info: true
|
|
hide_stats_info: true
|
|
quote_all: true
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
As you can see we now create a filter named `fix_rotation` of type `rot_footprint`:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
- name: fix_rotation
|
|
comment: 'Adjust rotation for JLC'
|
|
type: rot_footprint
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Using it, instead of the internal filter named `_rot_footprint`, is the same here. But you can then customize the filter.
|
|
|
|
The filter supports the following options:
|
|
|
|
- `extend`: [boolean=true] Extends the internal list of rotations with the one provided. Otherwise just use the provided list.
|
|
- `negative_bottom`: [boolean=true] Rotation for bottom components is computed via subtraction as `(component rot - angle)`. Note that this should be coherent with the `bottom_negative_x` of the position output.
|
|
- `invert_bottom`: [boolean=false] Rotation for bottom components is negated, resulting in either: `(- component rot - angle)` or when combined with `negative_bottom`, `(angle - component rot)`.
|
|
- `rotations`: [list(list(string))] A list of pairs regular expression/rotation. Components matching the regular expression will be rotated the indicated angle. Special names `_top` and `_bottom` will match all components on that side of the board.
|
|
|
|
In order to add a new rotation or just change an existing one you just need to use the `rotations` option.
|
|
As an example: the internal list of rotations rotates QFN packages by 270 degrees, no suppose you want to rotate them just 90 degrees.
|
|
The filter will look like this:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
- name: fix_rotation
|
|
comment: 'Adjust rotation for JLC'
|
|
type: rot_footprint
|
|
rotations:
|
|
- ["^QFN-", 90.0]
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This regular expression will match any footprint starting with `QFN-` and rotate it 90 degrees.
|
|
|
|
The internal list of rotations is:
|
|
|
|
| Footprint | Rotation |
|
|
| :-------------------------------------------------- | -------: |
|
|
|`^Bosch_LGA-8_2x2.5mm_P0.65mm_ClockwisePinNumbering` | 90.0 |
|
|
|`^R_Array_Convex_` | 90.0 |
|
|
|`^R_Array_Concave_` | 90.0 |
|
|
|`^SOT-223` | 180.0 |
|
|
|`^SOT-23` | 180.0 |
|
|
|`^TSOT-23` | 180.0 |
|
|
|`^SOT-353` | 180.0 |
|
|
|`^QFN-` | 270.0 |
|
|
|`^LQFP-` | 270.0 |
|
|
|`^TQFP-` | 270.0 |
|
|
|`^SOP-(?!18_)` | 270.0 |
|
|
|`^TSSOP-` | 270.0 |
|
|
|`^DFN-` | 270.0 |
|
|
|`^SOIC-` | 270.0 |
|
|
|`^VSSOP-10_` | 270.0 |
|
|
|`^CP_EIA-3216-18_` | 180.0 |
|
|
|`^CP_EIA-3528-15_AVX-H` | 180.0 |
|
|
|`^CP_EIA-3528-21_Kemet-B` | 180.0 |
|
|
|`^CP_Elec_8x10.5` | 180.0 |
|
|
|`^CP_Elec_6.3x7.7` | 180.0 |
|
|
|`^CP_Elec_8x6.7` | 180.0 |
|
|
|`^CP_Elec_8x10` | 180.0 |
|
|
|`^(.*?_\|V)?QFN-(16\|20\|24\|28\|40)(-\|_\|$)` | 270.0 |
|
|
|`^PowerPAK_SO-8_Single` | 270.0 |
|
|
|`^HTSSOP-28-1EP_4.4x9.7mm*` | 270.0 |
|
|
|
|
### XYRS files
|
|
|
|
XYRS files are just BoM files in CSV format that includes pick and place data (**X** position, **Y** position, **R**otation and **S**ide).
|
|
You can generate them using the internal BoM generator (`bom` output).
|
|
The following fields contains the needed information:
|
|
|
|
- `Footprint X`
|
|
- `Footprint Y`
|
|
- `Footprint Rot`
|
|
- `Footprint Side`
|
|
|
|
Additionally we support:
|
|
|
|
- `Footprint Type` (SMD, THT, VIRTUAL)
|
|
- `Footprint X-Size`
|
|
- `Footprint Y-Size`
|
|
- `Footprint Populate`
|
|
|
|
Important: These files doesn't support manual panelization with repeated reference names, you'll get the coordinates for just one component because this is a BoM.
|
|
|
|
## Notes about 3D models
|
|
|
|
This section contains some notes and advices about the use of 3D models.
|
|
There are many strategies and you can choose the mix that better suits your needs.
|
|
If you have any suggestion don't hesitate in contacting me to add them.
|
|
|
|
### 3D models and docker images
|
|
|
|
The default KiCad 3D models aren't included in the KiBot docker images.
|
|
This is because the 3D models currently needs around 5 GB and the current docker images are between 1 and 1.6 GB.
|
|
So adding them means a huge increase in size.
|
|
|
|
This is not a big problem because KiBot will download any missing 3D model from KiCad's repo.
|
|
|
|
As a side effect you'll get errors and/or warnings about the missing 3D models and/or KiCad environment variables pointing to them.
|
|
|
|
If you need to install the KiCad 3D models in one of the `kicad_debian`, `kicad_auto` or `kicad_auto_test` images just run the
|
|
`/usr/bin/kicad_3d_install.sh` script included with the current images.
|
|
|
|
If you are running the Github action and you want to install the KiCad 3D models use the `install3D: YES` option.
|
|
|
|
### Self contained projects
|
|
|
|
Try to make your project self contained.
|
|
If you are using a repo this means the repo should contain anything needed to work with your project.
|
|
|
|
KiCad 6 helps a lot in this regard. Now schematic files are self contained, you don't need external files to work with them.
|
|
Even with this I think including the used symbols and footprints isn't a bad idea.
|
|
If you expect other people to edit your project then is much simpler if the originals are in the project.
|
|
|
|
The 3D models are a very special case. KiCad doesn't help much in this regard.
|
|
I strongly suggest including all used 3D models in your repo.
|
|
You can then use `${KIPRJMOD}` as base for the path to the models, this will be expanded to the current path to your project.
|
|
So you can use things like `${KIPRJMOD}/3D/MODEL_NAME` and store all the 3D models in the *3D* folder inside your project folder.
|
|
|
|
### 3D models aliases
|
|
|
|
This is a very limited feature in KiCad. You can define an `ALIAS` and then use `ALIAS:MODEL_NAME`.
|
|
The `ALIAS` will say where to look for `MODEL_NAME`. This looks coherent with the way KiCad handles symbols and footprints.
|
|
But it currently has a huge limitation: this information is stored along with the user configuration and there is no way to
|
|
complement it at project level. I don't recommend using aliases because it makes quite complicated to create self contained
|
|
projects.
|
|
|
|
KiBot offers some mechanisms to help using aliases:
|
|
|
|
1. You can define your aliases in the `global` section using the `aliases_for_3d_models` option.
|
|
2. You can use environment and text variables to define aliases. This can be disabled using the `disable_3d_alias_as_env` option.
|
|
|
|
The problem with this is that you must keep two lists synchronized, one for KiCad and the other to make your project self contained.
|
|
|
|
### How to handle addons
|
|
|
|
KiCad 6 introduces a *Plugin and Content Manager*, they can contain footprints and 3D models.
|
|
Using 3D models aliases looks like a good solution here, but this isn't.
|
|
The best solution here is to use the `KICAD6_3RD_PARTY` variable.
|
|
Instead of defining an alias pointing to the content you can just use `${KICAD6_3RD_PARTY}/3dmodels/FULL_PLUGIN_NAME/MODEL_NAME`.
|
|
I know this is long, but this will make your project portable.
|
|
The user will need to download the plugin, but won't need to define any alias.
|
|
|
|
### Getting a self contained PCB
|
|
|
|
In order to help users to create self contained projects KiBot offers some help.
|
|
The following configuration:
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
# Example KiBot config file
|
|
kibot:
|
|
version: 1
|
|
|
|
outputs:
|
|
- name: export_pcb
|
|
comment: 'Copy 3D models'
|
|
type: copy_files
|
|
dir: 'expoted_pcb'
|
|
options:
|
|
files:
|
|
- source_type: 3d_models
|
|
dest: 3d_models+
|
|
save_pcb: true
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Will create a new PCB inside a directory called `expoted_pcb`, this PCB will use the 3D models copied to `expoted_pcb/3d_models` using
|
|
relative paths. So you can move the new PCB file to any place, as long as the `3d_models` directory is in the same place as the PCB.
|
|
|
|
## Credits
|
|
|
|
- **KiBot project**: Salvador E. Tropea (@set-soft)
|
|
- **Original KiPlot project**: John Beard (@johnbeard)
|
|
- **Original KiCad Automation Scripts**: Scott Bezek, Productize SPRL
|
|
- **KiBoM**: Oliver Henry Walters (@SchrodingersGat)
|
|
- **Interactive HTML BoM**: @qu1ck
|
|
- **PcbDraw**: Jan Mrázek (@yaqwsx)
|
|
- **KiCost**: Dave Vandenbout (@devbisme) and Hildo Guillardi Júnior (@hildogjr)
|
|
- **KiCAD to Boardview exporter**: @whitequark
|
|
- **S-expression parser**: Takafumi Arakaki
|
|
- **Python macros**: Juha Jeronen (@Technologicat)
|
|
- **Board2Pdf**: Albin Dennevi
|
|
- **PyPDF2**: Mathieu Fenniak
|
|
- **svgutils**: Bartosz Telenczuk (@btel)
|
|
- **Contributors**:
|
|
- **Error filters ideas**: Leandro Heck (@leoheck)
|
|
- **GitHub Actions Integration/SVG output**: @nerdyscout
|
|
- **Plug-in loader fix**: Stavros Korokithakis (@skorokithakis)
|
|
- **SCH loader fix**: @Sabolik
|
|
- **SCH library loader fix**: Bernhard B. (@bbernhard)
|
|
- **GitHub Actions fix**: @TheSlowGrowth
|
|
- **Easier README navigation**: Robin Vobruba (@hoijui)
|
|
- **Typos corrections**: Seth Kaz (@sethkaz) and Sebastian Grau (@SebastianGrau)
|
|
- **Various tools suggested**: MDW (@mdeweerd)
|
|
- **Various tools suggested**: Chris Wilson (@cdwilson)
|
|
- **GENCAD export for KiAuto**: Theo Hussey (@flaminggoat)
|
|
- **Various fixes**: Henning Kleen (@hkleen)
|
|
- **SCH print all-pages option**: Kevin Dong (@kevin-dong-nai-jia)
|
|
- **Sources of inspiration and good ideas**:
|
|
- **JLC Kicad Tools**: Matthew Lai (@matthewlai)
|
|
- **KiCad Gerber Zipper**: @g200kg
|
|
- **pimpmykicadbom**: Anton Savov (@antto)
|
|
- **Others**:
|
|
- **Robot in the logo**: Christian Plaza (from pixabay)
|
|
- **Robot arm in assembly_simple.svg**: [Pixlok](https://pixlok.com/)
|
|
- **Chip in assembly_simple.svg**: [oNline Web Fonts](https://www.onlinewebfonts.com/)
|
|
- **Wrench**: [Freepik - Flaticon](https://www.flaticon.es/iconos-gratis/llave-inglesa)
|
|
- **Most icons for the navigate_results output**: The KiCad project
|